Concrete Technology
Design Principles of Concrete Structures
-
-
Concrete Structures (Part-I) by Zahid Ahmad Siddiqi
.References
- Reinforced Concrete (6th Edition) by Edward G. Nawy
-
Design of Concrete Structures (14th Edition)
by Arthur H. Nilson, David Darwin & Charles W. Dolan
- Building Code Requirements for Structural Concrete
- Reinforced Concrete (6th Edition) by Edward G. Nawy
-
(ACI 318-19)
Concrete
Concrete
Concrete is a mixture of cement, fine and coarse aggregate.
Concrete mainly consists of a binding material and filler material.
If filler material size is < 4.75 mm it is fine aggregate and > 4.75mm is coarse aggregate. (ASTM Sieve #4)
Concrete
Plain Cement Concrete (PCC)
Mixture of cement , sand and coarse aggregate without any reinforcement is known as PCC.
PCC is strong in compression and week in tension. Its tensile strength is so small that it can be neglected in design.
Reinforced Cement Concrete (RCC)
Mixture of cement , sand and coarse aggregate with
reinforcement is known as RCC. (Tensile strength is improved)
Concrete
Common Mix Proportion
Cement : Sand : Crush
1 :1.5 :31 :2 :4
Water Cement Ratio (W/C)1 :4 :8W/C = 0.5 – 0.6
For a mix proportion of 1:2:4 and W/C = 0.5, if cement is 50 kg
Sand= 2 x 50 = 100 KgCrush Water= 4 x 50 = 200 Kg
= 50 x 0.5 = 25 KgBatching By WeightBatching by Weight

Classification of Grades of Concrete


Batching by Volume
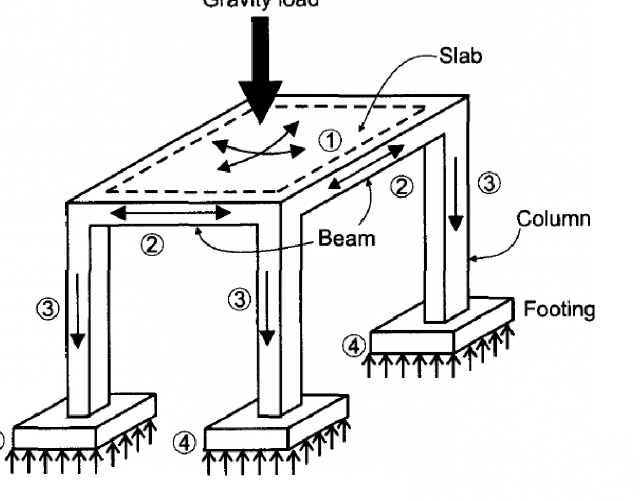
Mechanism of Load Transfer
Function of structure is to transfer all the loads safely to ground.
A particular structural
Roof Slab
Load
Roof Surface
member transfers load to other structural member.
Beams
Column
Foundation
Sub Soil
Mechanism of Load Transfer
Mechanism of Load Transfer


Merits of Concrete Construction
Good Control over cross sectional dimensions and Shape One of the major advantage of concrete structures is the full control over the dimensions and structural shape. Any size and shape can be obtained by preparing the formwork accordingly.
-
Availability of Materials
All the constituent materials are earthen materials (cement, sand, crush) and easily available in abundance.
-
Economic Structures
All the materials are easily available so structures are economical.
-
Good Insulation
Concrete is a good insulator of Noise & heat and does not allow them to transmit completely.
Merits of Concrete Construction (contd…)
-
Good Binding Between Steel and Concrete
there is a very good development of bond between steel and concrete.
-
Stable Structure
Concrete is strong in compression but week in tension and steel as strong in tension so their combination give a strong stable structure.