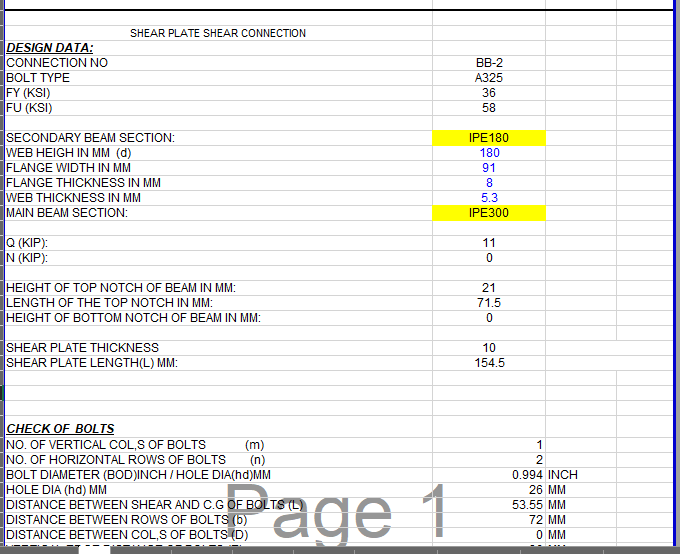
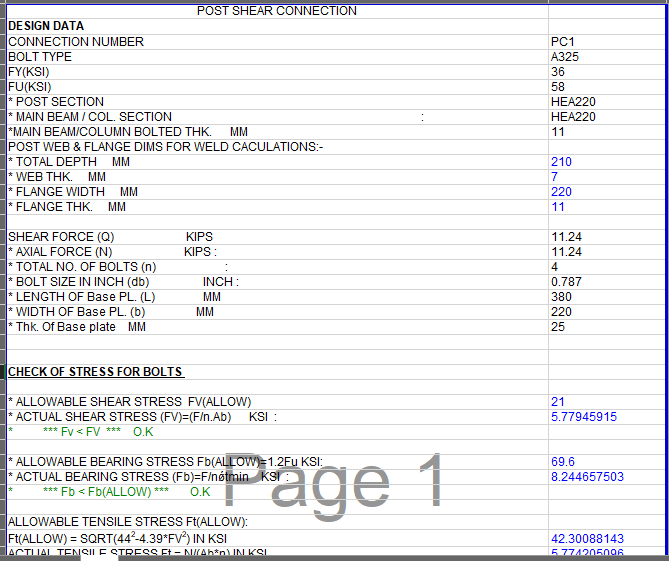
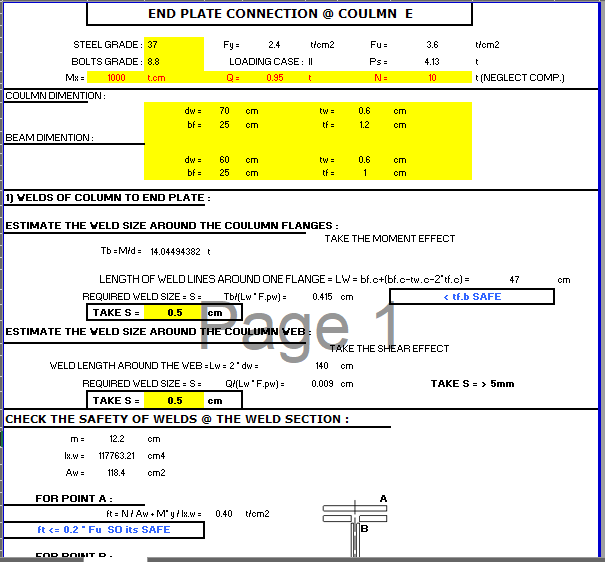
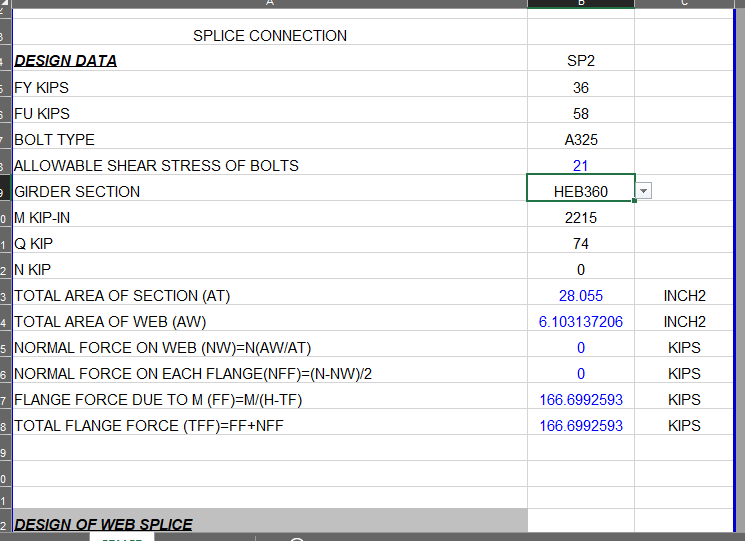
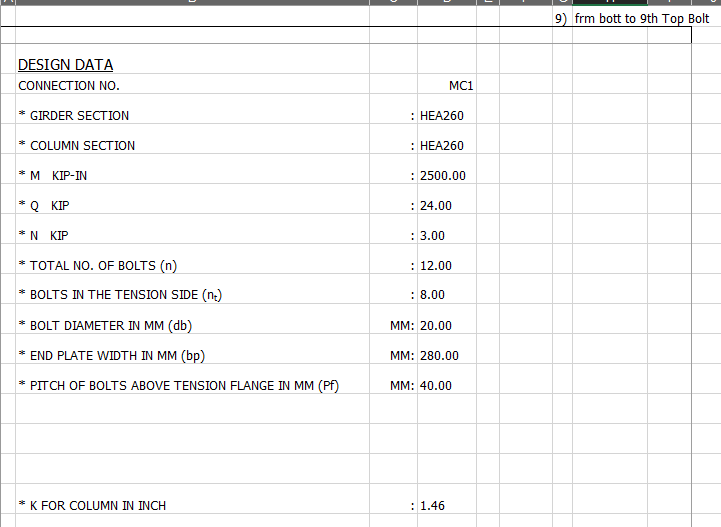
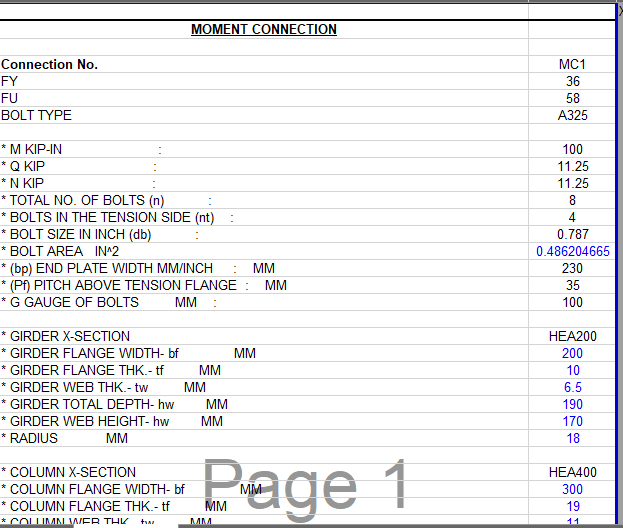
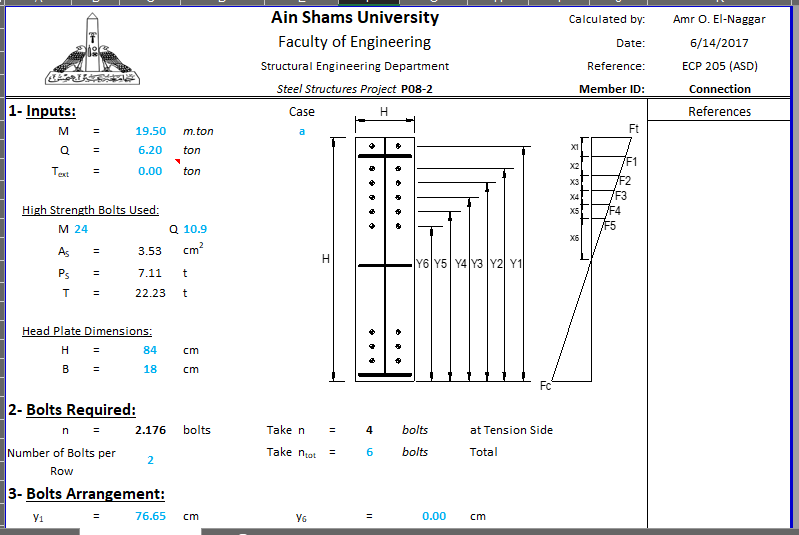
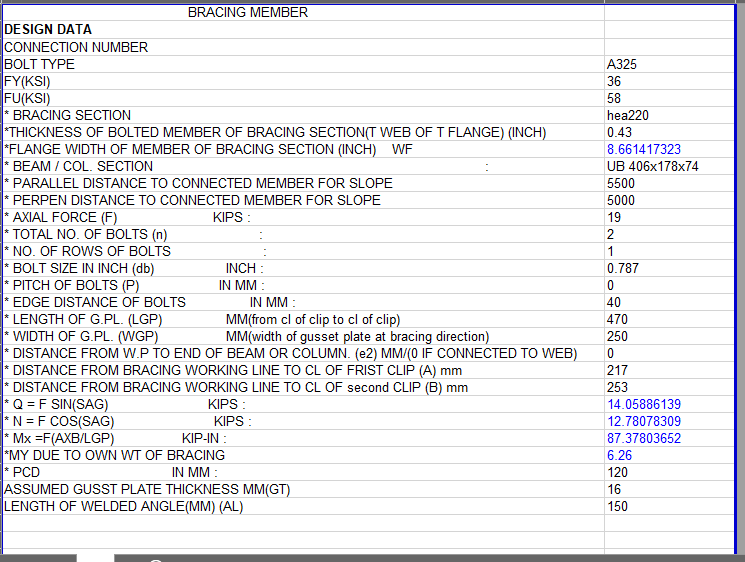
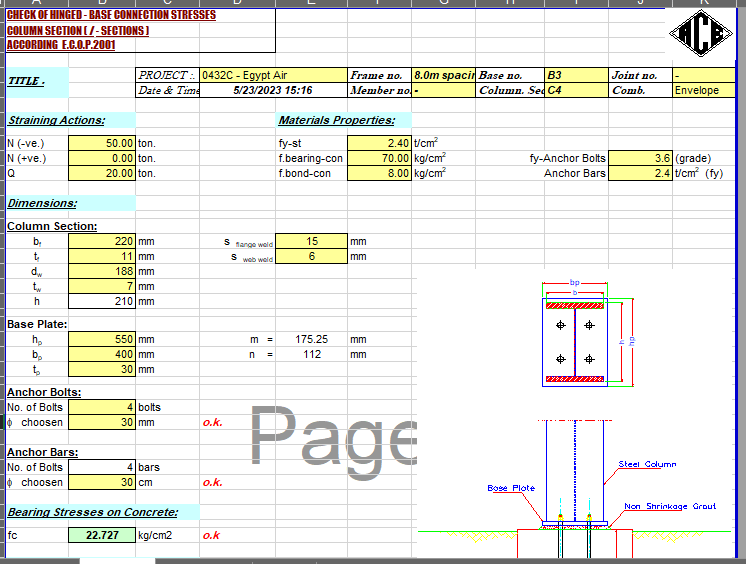
SHEAR PLATE SHEAR CONNECTION
A shear plate shear connection, also known as a shear tab or shear plate connection, is a type of connection used to transfer shear forces between a steel beam and a column or other structural member. It consists of a plate that is welded or bolted to the beam flange and connected to the column […]
SHEAR PLATE SHEAR CONNECTION Read More »