Ground Improvement Technology
Why Ground improvement?
- Increases shear strength
- Reduces permeability, and
- Reduces compressibility
Understanding Ground Improvement
-
Ground improvement includes two parts.
1.First Understand the ground
2.Then find out the most engineered1 solution for improvement
- Engineered means most economical, safe and ease of simplicity to adopt
Methods for Soil Improvement?
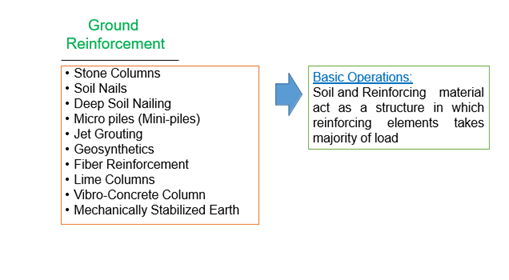
Ground Reinforcement
- Stone Columns
- Soil Nails
- Deep Soil Nailing
- Micro piles (Mini-piles)
- Jet Grouting
- Ground Anchors
- Geosynthetics
-
Fiber Reinforcement
Ground Improvement
- Deep Dynamic Compaction
- Drainage/Surcharge
- Compaction grouting
-
Surface Compaction
Ground Treatment
- Soil Cement
- Lime Admixtures
- Fly ash
- Dewatering
- Soil Cement
Tilting of structure: Overturning



Leaning temple dome, Huma, Orissa, India
A building at the Lotus Riverside complex in Shanghai’s Minhang district collapsed
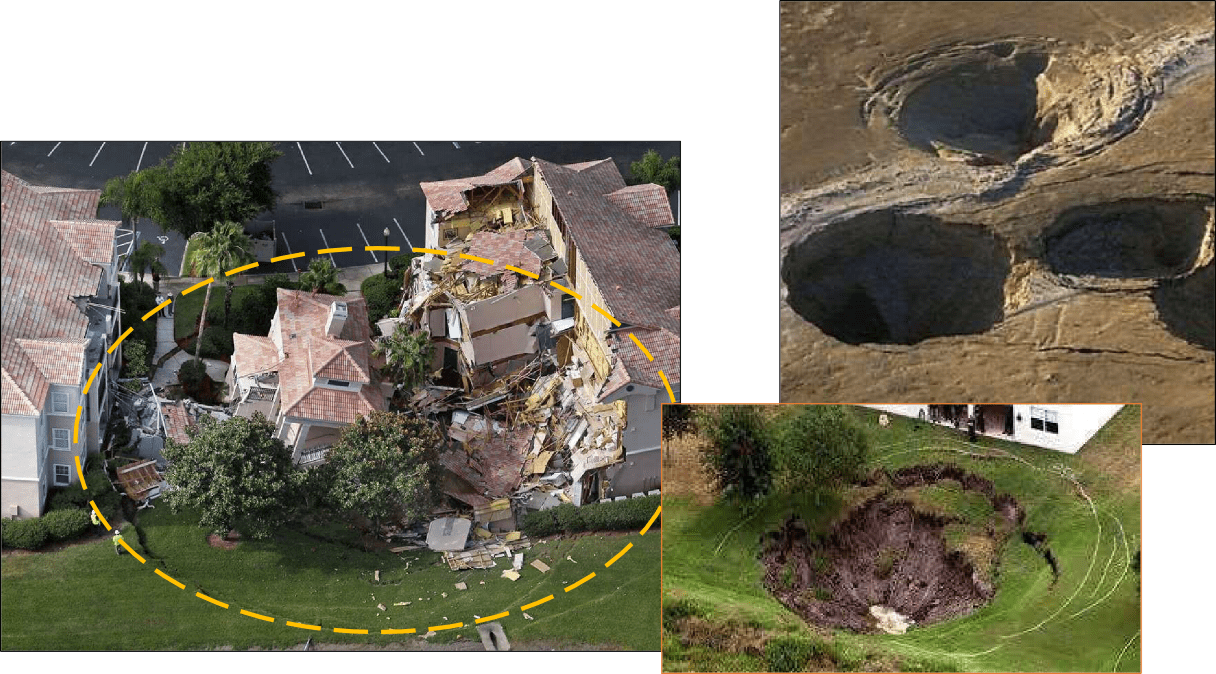
Sink Holes
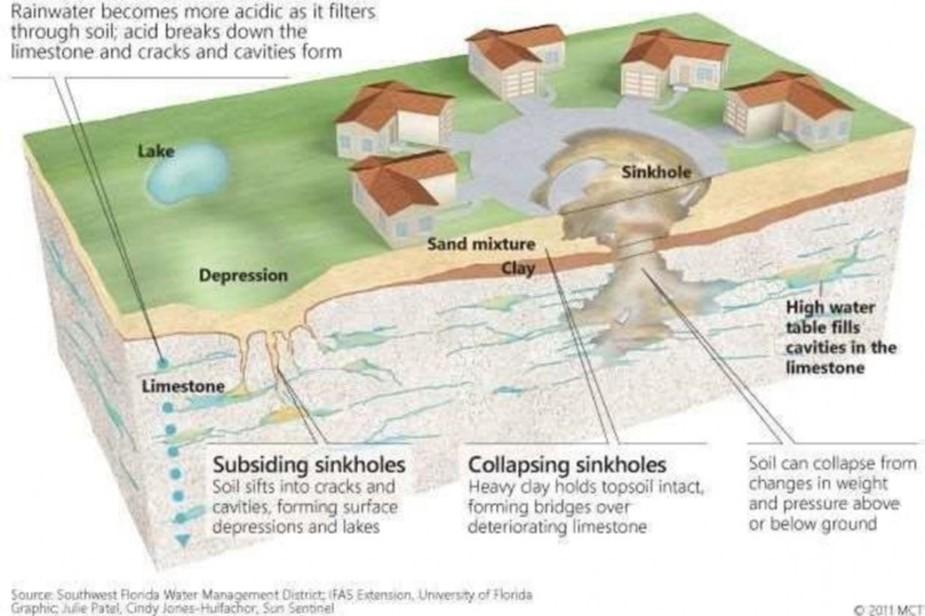 Formation of Sink Holes
Formation of Sink Holes

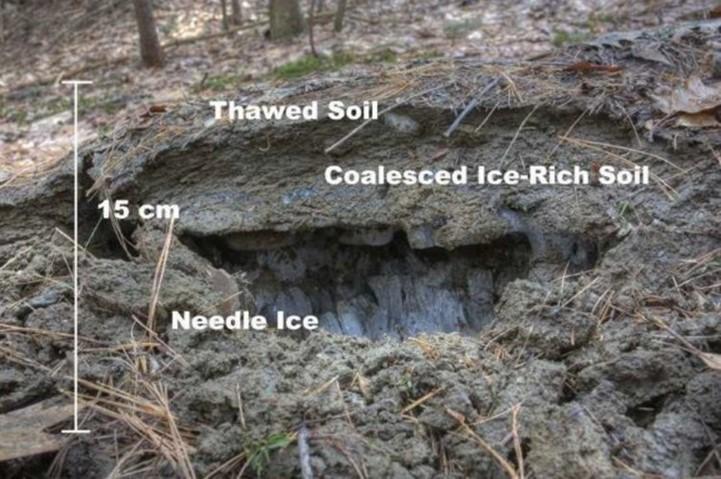
Frost heave

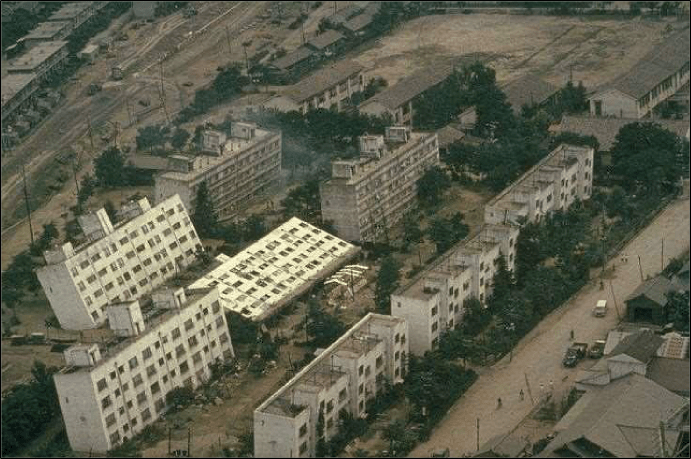
Overturned apartment complex, Niigata 1964

Why we study geotechnical Structure Failure?
- Because we want engineered design of geotechnical structures.
- Engineered means
- Economical
- Safe
- Durable
- Strong
List of ground improvement techniques
Ground Improvement
-
Deep Dynamic
Compaction
- Drainage/Surcharge
- Electro-osmosis
- Compaction grouting
- Blasting
- Surface Compaction
- Ground Freezing
Basic Operations:
Increasing soil Density Removing Air Voids, Pore water Changing soil water properties
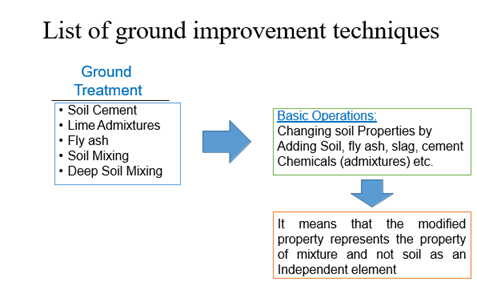
List of ground improvement techniques
Ground
Improvement
Field Compaction
Equipment
Smooth-wheel roller (drum)
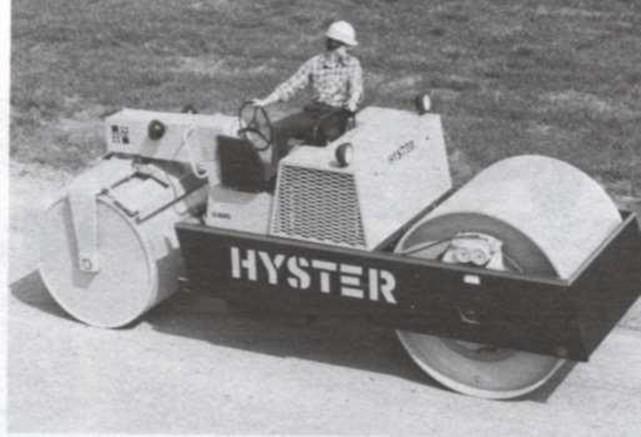

- 100% coverage under the wheel
-
Can be used on all soil types
except for rocky soils.
-
The most common use of large smooth wheel rollers is for proof- rolling subgrades and compacting asphalt pavement.
-
Now a days Vertical vibrator is also attached to smooth wheel rollers.
Equipment (Cont.)
Pneumatic (or rubber-tired) roller
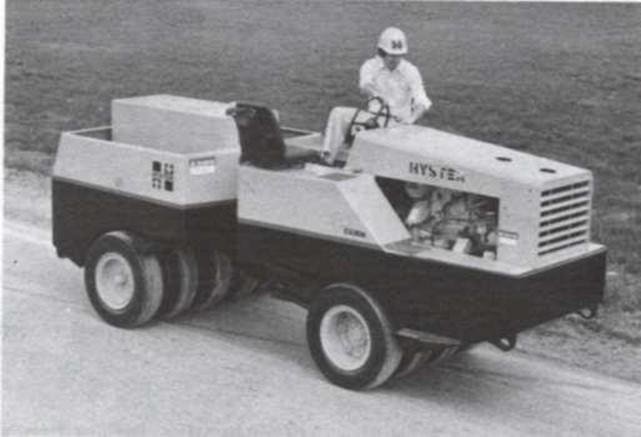

- 80% coverage under the wheel
-
Can be used for both granular and
fine-grained soils.
- Can be used for highway fills or earth dam construction.
- 80% coverage under the wheel
Equipment (Cont.)
Sheepsfoot rollers
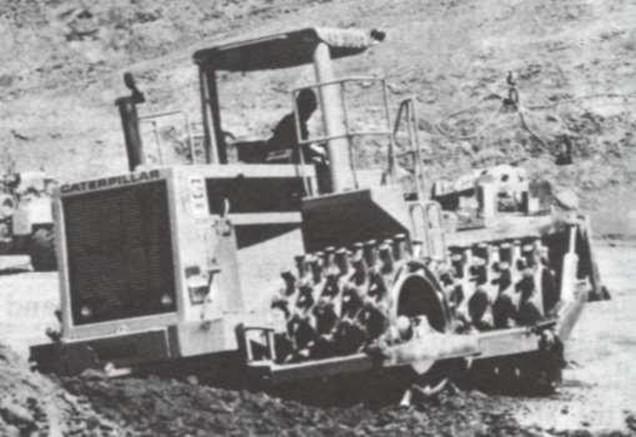
-
Has many round or rectangular shaped protrusions or “feet” attached to a steel drum
- 8% ~ 12 % coverage
-
It is best suited for clayed soils.
Equipment (Cont.)
Tamping foot roller
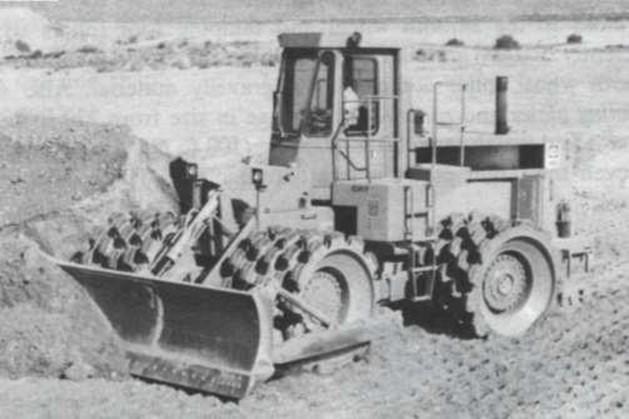

- About 40% coverage
- It is best for compacting fine-
- About 40% coverage
grained soils (silt and clay).
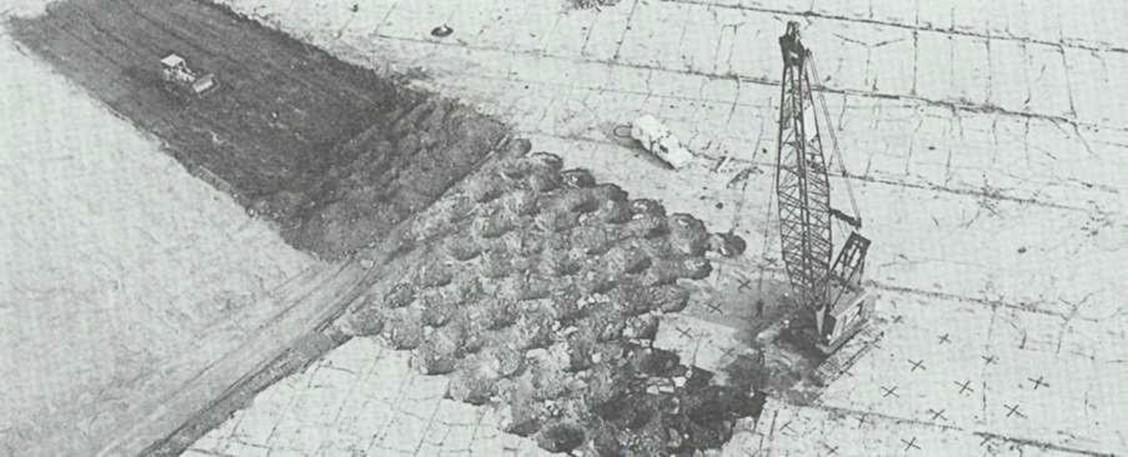
Dynamic Compaction
-
When
- Existing surface or near-surface soil is poor with regard to foundation support
- Existing surface or near-surface soil is poor with regard to foundation support
-
For which soil?
- Both cohesive and cohesionless soils
- Both cohesive and cohesionless soils
-
How
- Drop a very heavy (2~20 tons) weight onto the soil from a relatively great height (20 ~ 100 ft)
-
Dropping weight randomly? → a closely spaced grid pattern is selected.
Dynamic Compaction
Dynamic compaction was first used in Germany in the mid-1930’s.
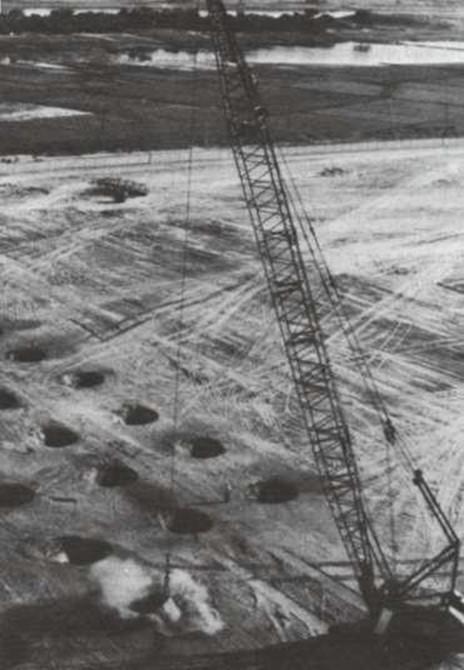

Dynamic Compaction
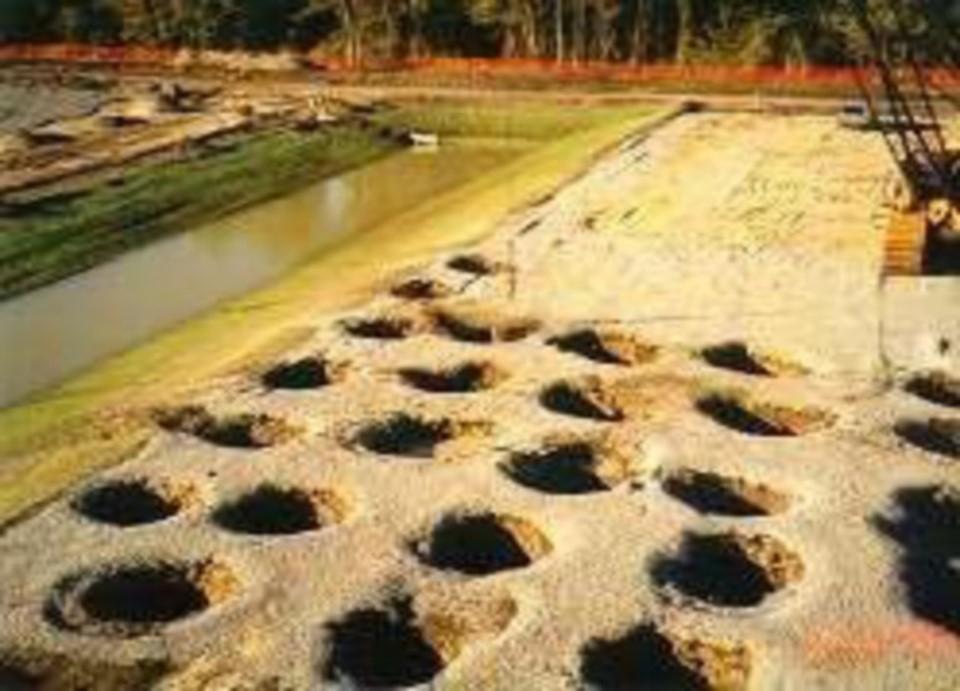

Vibro-Compaction
Vibroflotation
Vibroflotation is a technique for in situ densification of thick layers of loose granular soil deposits.
It was developed in Germany in the 1930s.

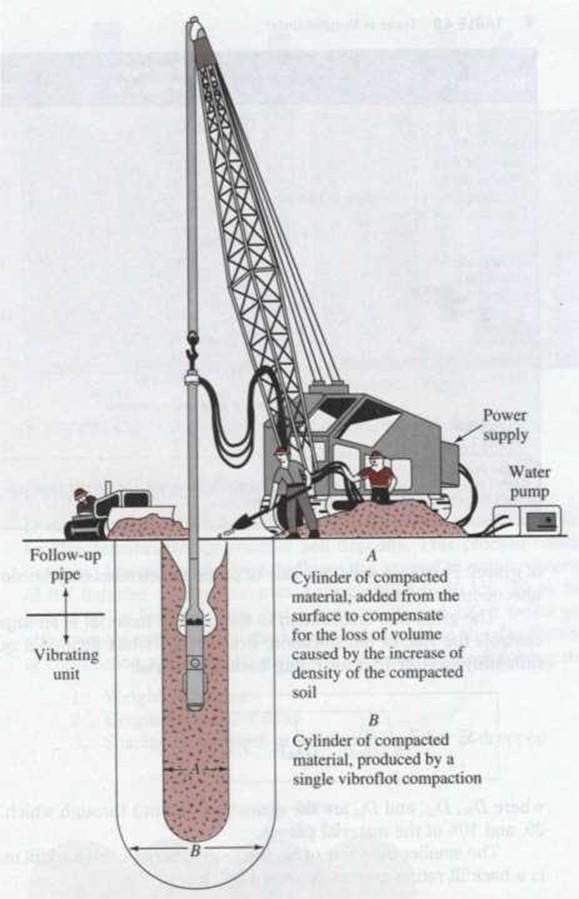
Vibroflotation Procedures
- Drop a very heavy (2~20 tons) weight onto the soil from a relatively great height (20 ~ 100 ft)
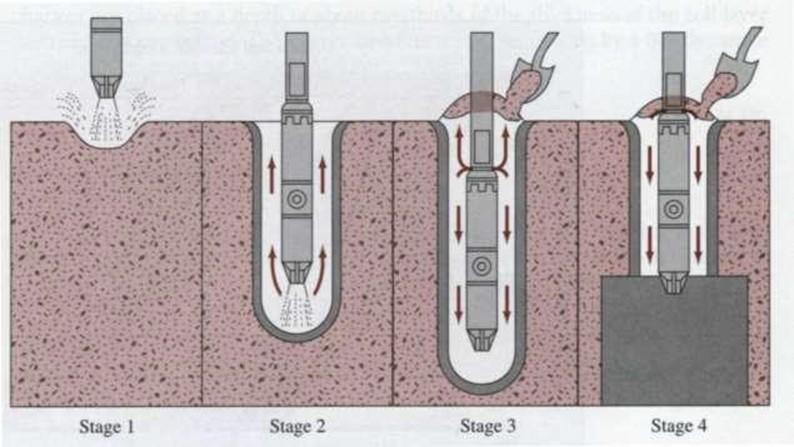
Stage1: The jet at the bottom of the Vibroflot is turned on and lowered into the ground
Stage2: The water jet creates a quick condition in the soil. It allows the vibrating unit to sink into the
ground
Stage 3: Granular material is poured from the top of the hole. The water from the lower jet is transferred to the jet at the top of the vibrating unit. This water carries the granular material down the hole
Stage 4: The vibrating unit is gradually raised in about 0.3-m lifts and held vibrating for about 30 seconds at each lift. This process compacts the soil to the desired unit weight.
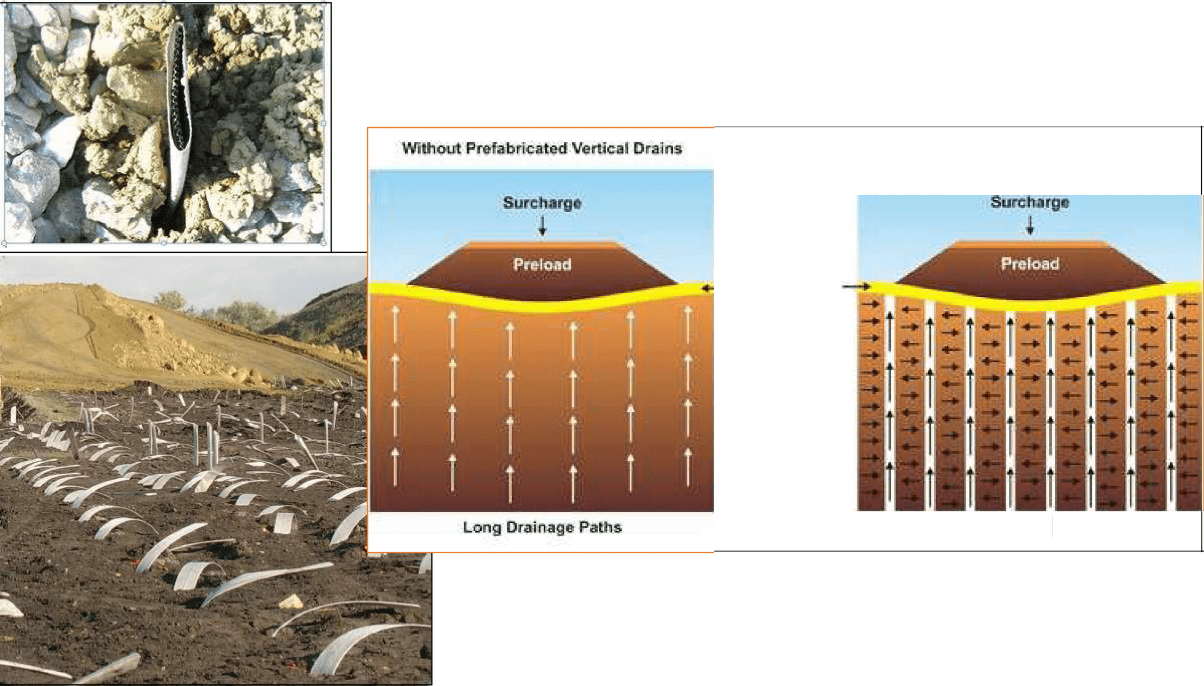
Pre-loading: Vertical Drains
Prefabricated Vertical Drains (PVDs) are composed of a plastic core encased by a geotextile for the purpose of expediting consolidation of slow draining soils.
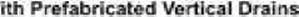

Ground Treatment
Soil-Cement stabilization
Stabilization Using cement and other admixtures such as fly ash, blast furnace slag has been adopted in many geotechnical and
highway engineering projects.
Soil Mixing & Deep Soil Mixing
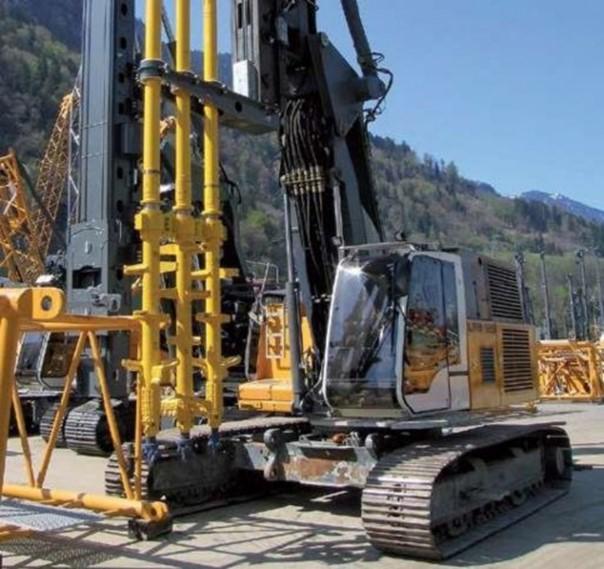


Mixing tools used for different soils



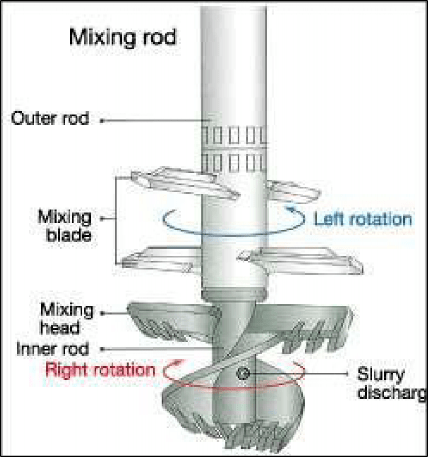
Process of deep soil Mixing
Ground
Reinforcement
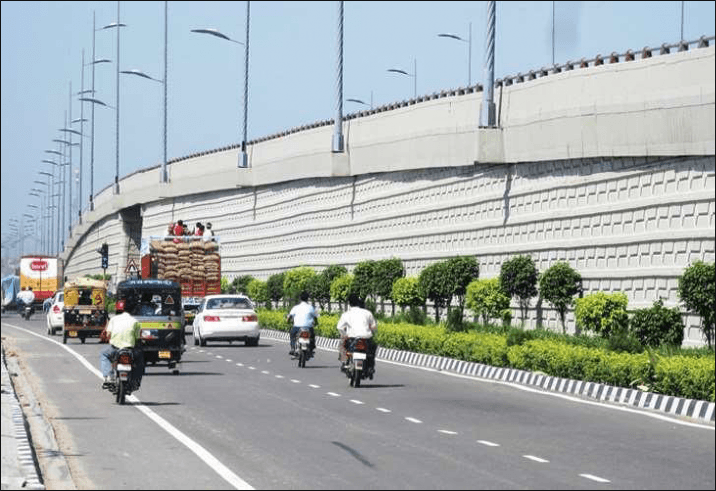
Mechanically Stabilized Soil
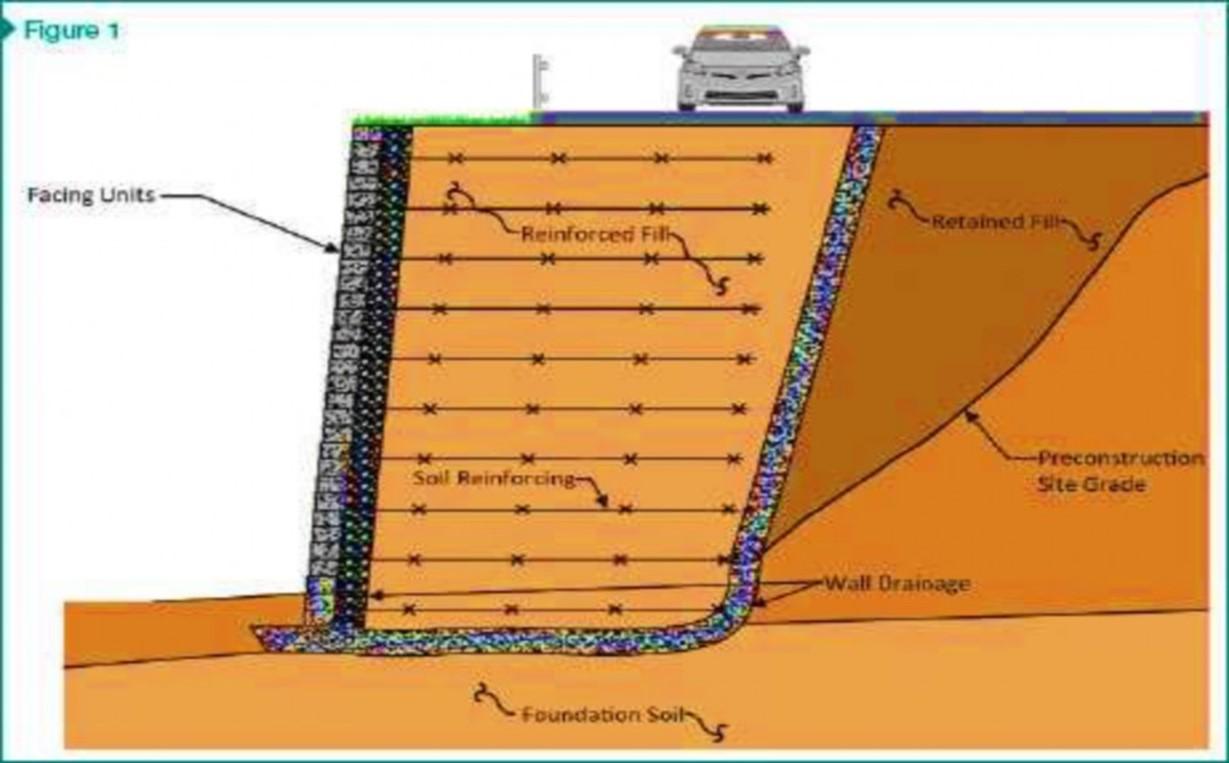
Elevated Highway,

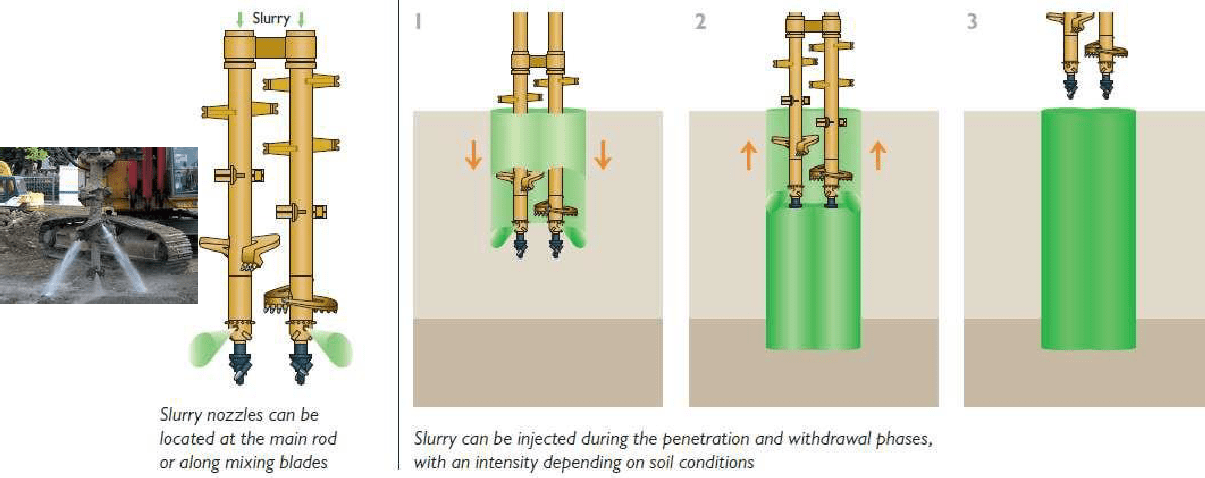
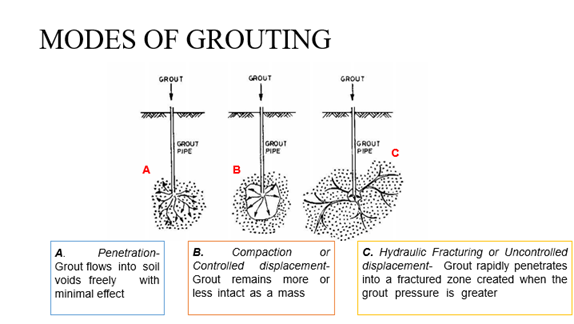
Grouting
-
Injection formation
of a slurry or a liquid solution into a soil or rock formation
- The grout subsequently hardens – increases the strength and decreases compressibility and permeability.
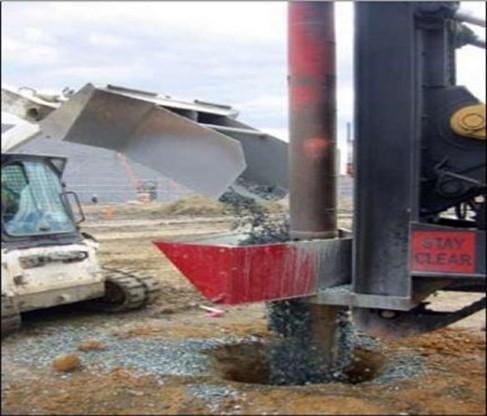
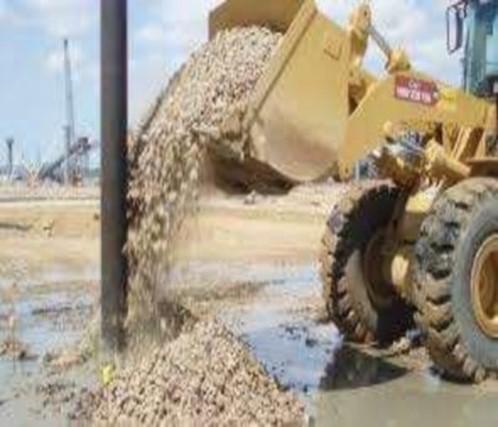
Stone Column
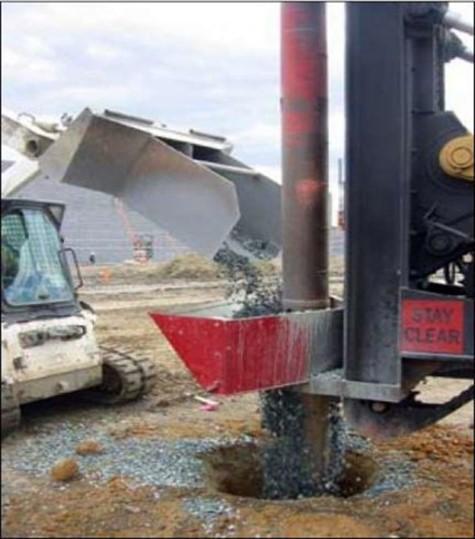

- Stone column consists of crushed coarse aggregates of various sizes
-
A ground improvement technique to improve the load bearing capacity and reduce the settlement of the soil
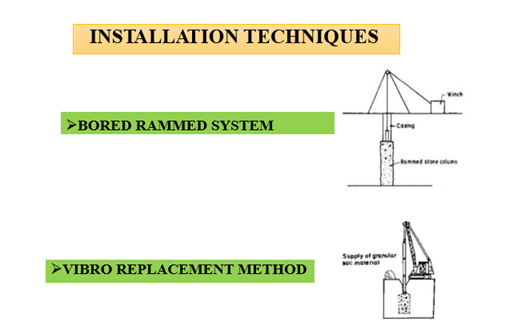
INSTALLATION TECHNIQUES
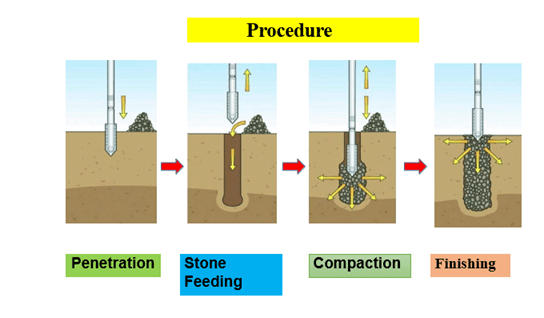



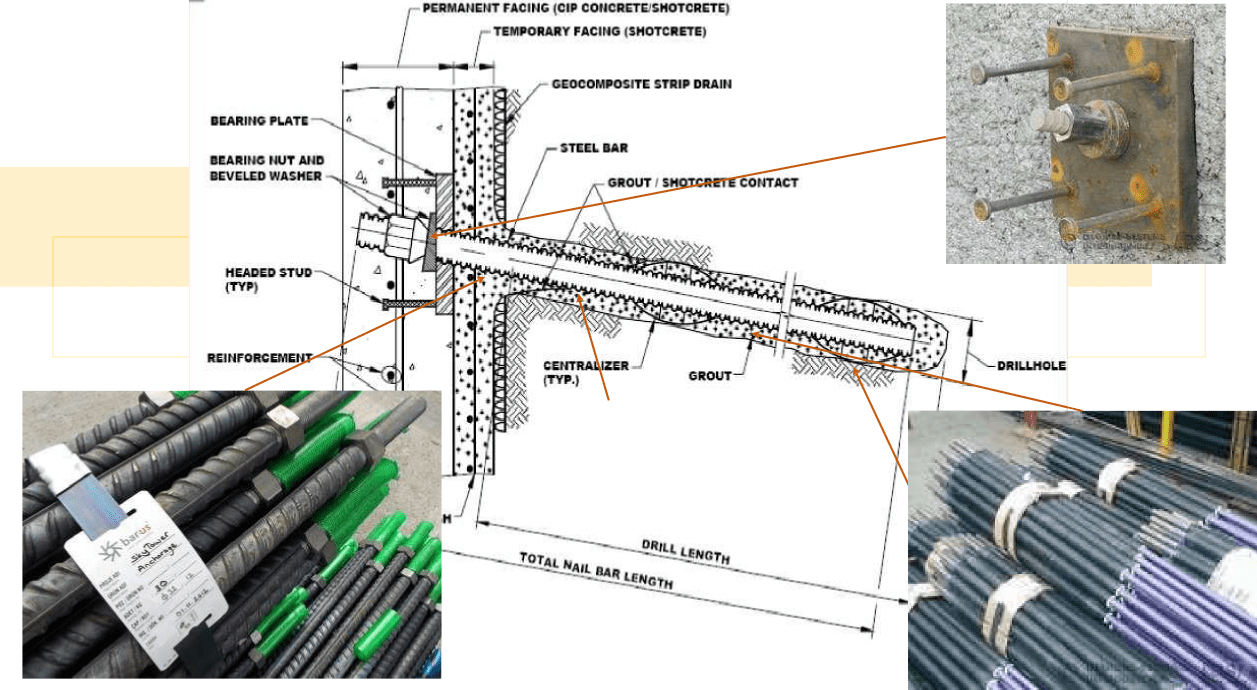
Soil nailing
INTRODUCTION
- Soil nailing is the method of reinforcing the soil with steel bars or other material.
CONSTRUCTION SEQUENCE
- Excavation of Slope
- Drilling Nail Holes
- Nail Installation and Grouting
- Construction of Temporary Shotcrete Facing
- Construction of Subsequent Level
-
Construction of a Final, Permanent Facing
Gabions
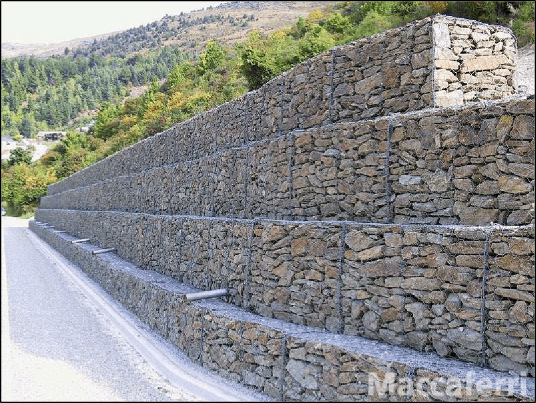
What are Gabions?
-
The term gabion refers to a modular containment system that enables rock, stone or other inert materials to be used as a construction material.
-

Micro piles
-
A micropile is a small-diameter (typically less than 300 mm), drilled and grouted replacement pile that is typically (up to 20% As/Ac) reinforced.
-
A micropile is constructed by drilling a borehole, placing reinforcement, and grouting the hole.
-
Micropiles can withstand axial and/or lateral loads.

Geosynthetics
What is a Geosynthetic ?
-
Natural or artificial product that is used along with soil in geotechnical constructions.
-
Natural: coir, jute, hemp, etc.
-
Artificial: polymeric or metallic
Types of Geo-Materials (Geosynthetics family)
- Geotextile.
- Geogrid.
- Geonet.
- Geo Membrane
- GeoComposites
- Geofoam
- Geocell
- Geomat
- Geomesh
- Geopipe
-
Geospacer
-
Geotextile
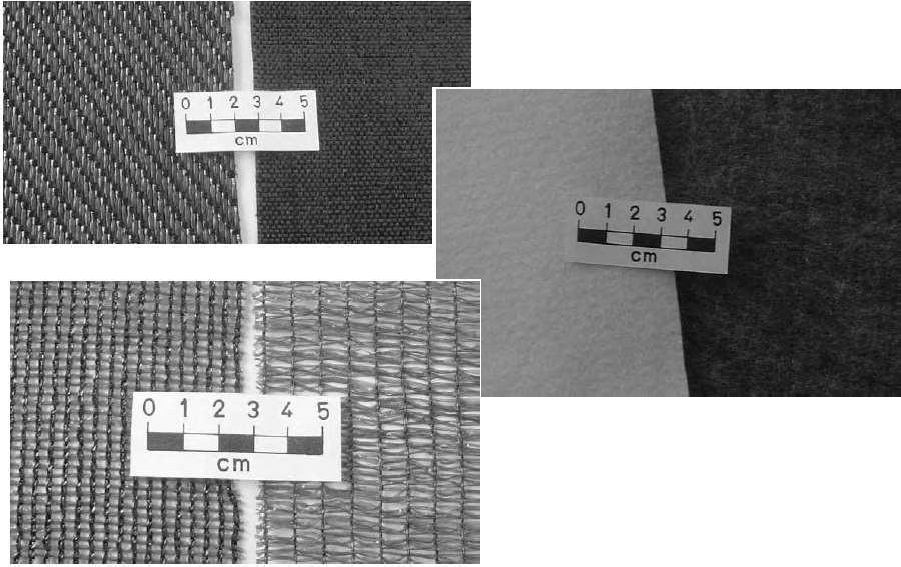 Geo Grid
Geo Grid
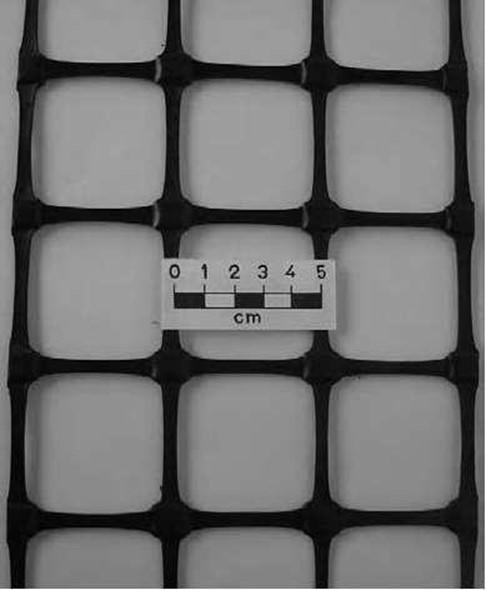
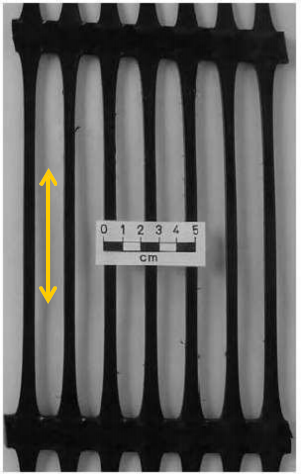

-
Uniaxial (ii) Biaxial
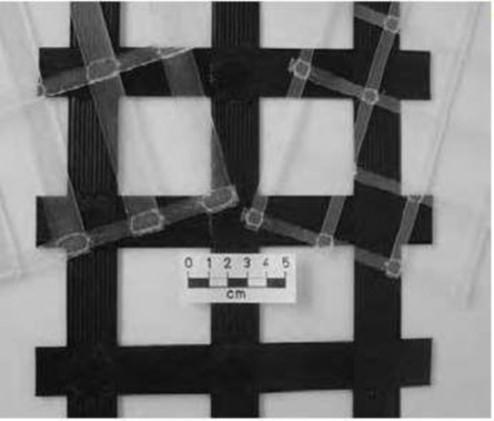

(iii) Bonded (iv) Woven
-
-
Geonet.

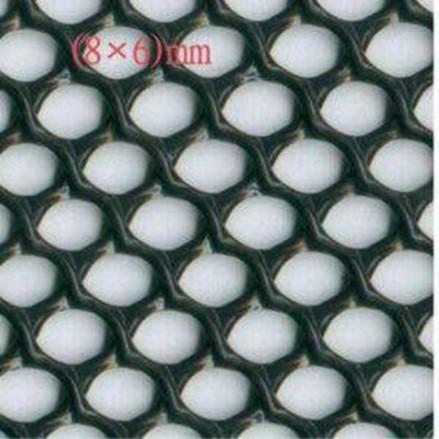
-
Geo Membrane
-
Geo-composites
-
Combination of one or more type of geosynthetics for modified function.

-
-
Geofoam
-
- Geotextile.
-
- Foam like material, provided for functions mentioned below:
- Moisture retention.
- Erosion protection.
- Generally gives temporary solution of the problem.
7.Geocell
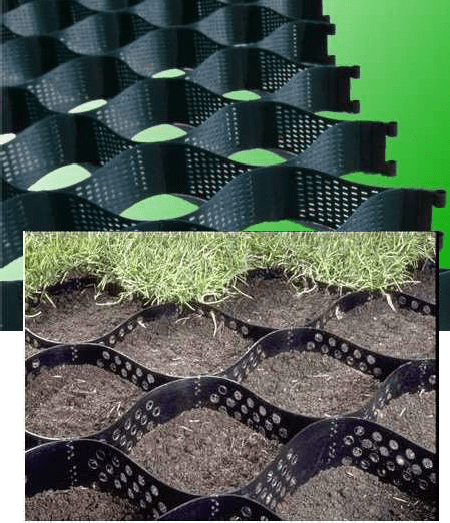

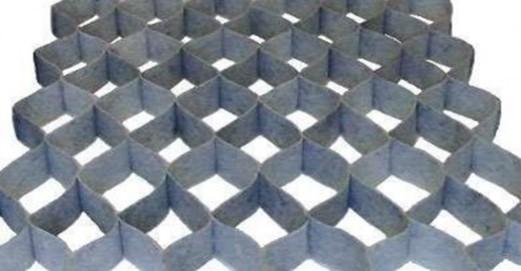

Geo Cell
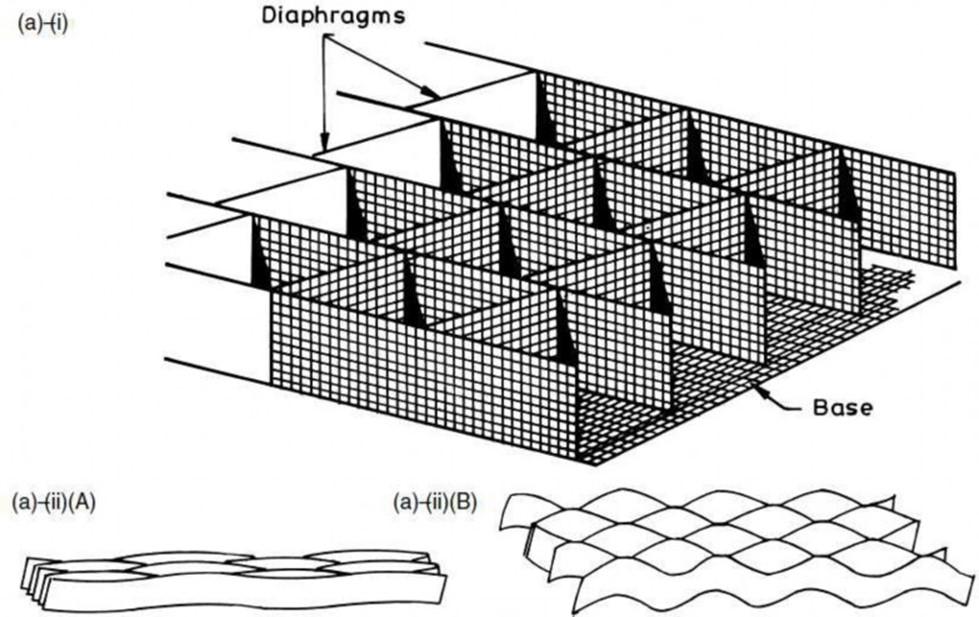
(a) Geocell – (i) site assembled, (ii) factory produced (A) collapsed form, (B) expanded form
8.Geomat
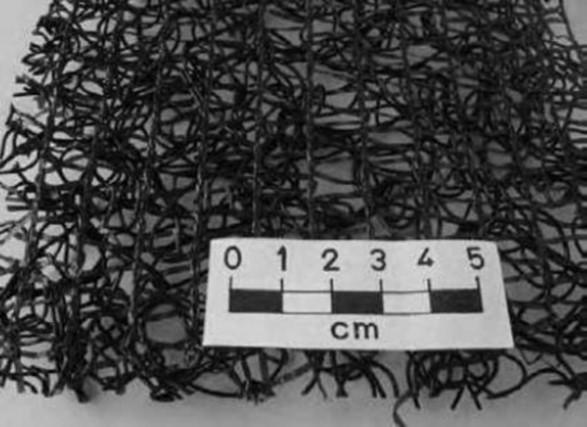


9.Geomesh
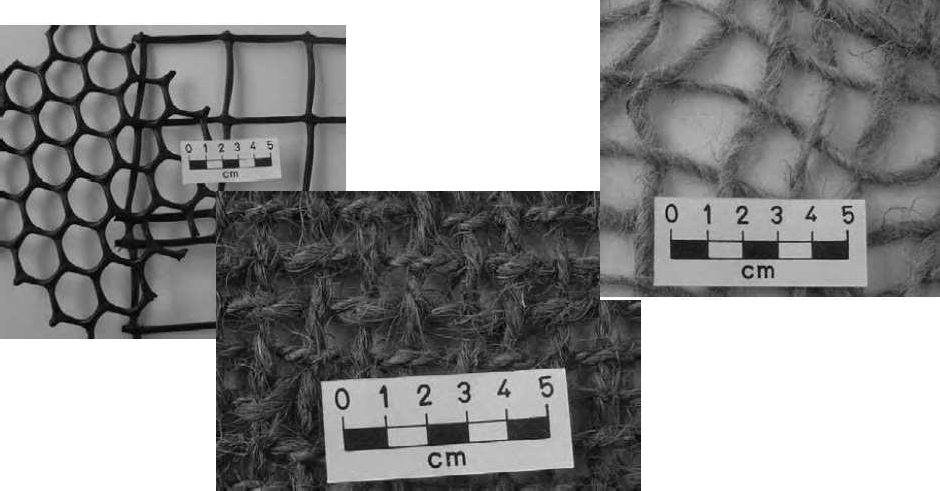

10.Geopipe
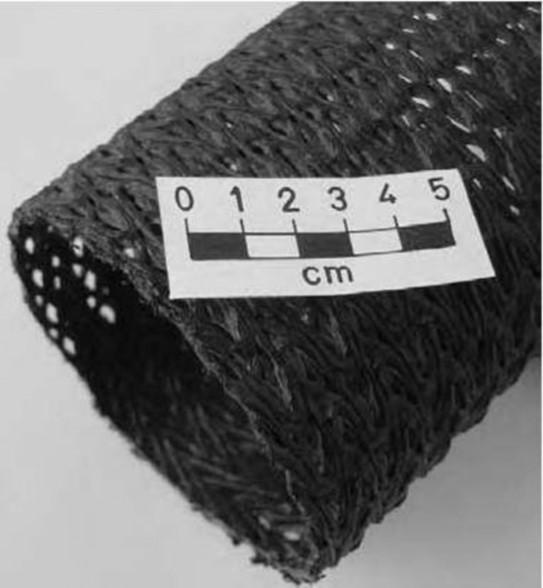


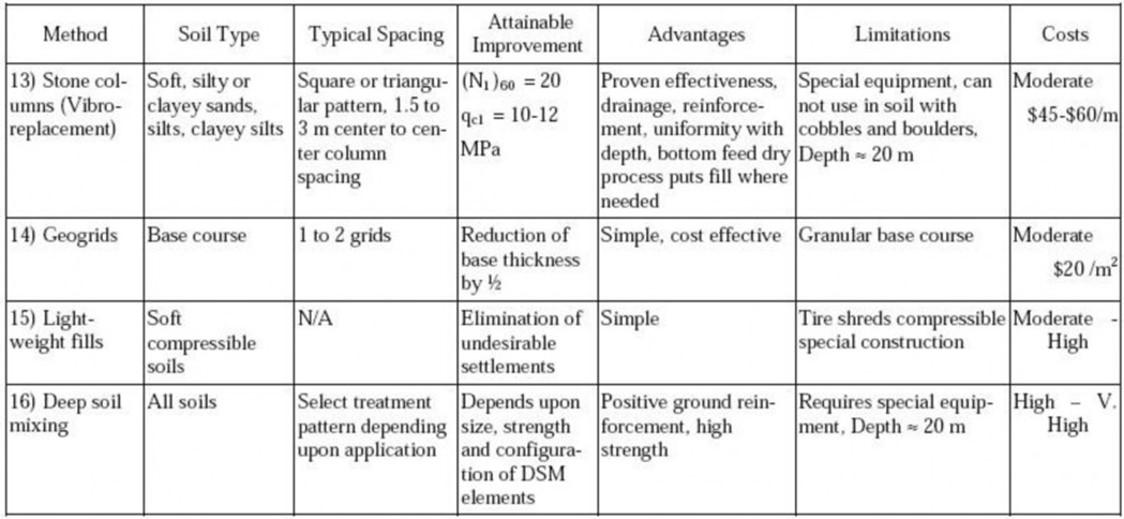
Summary of ground improvement Methods
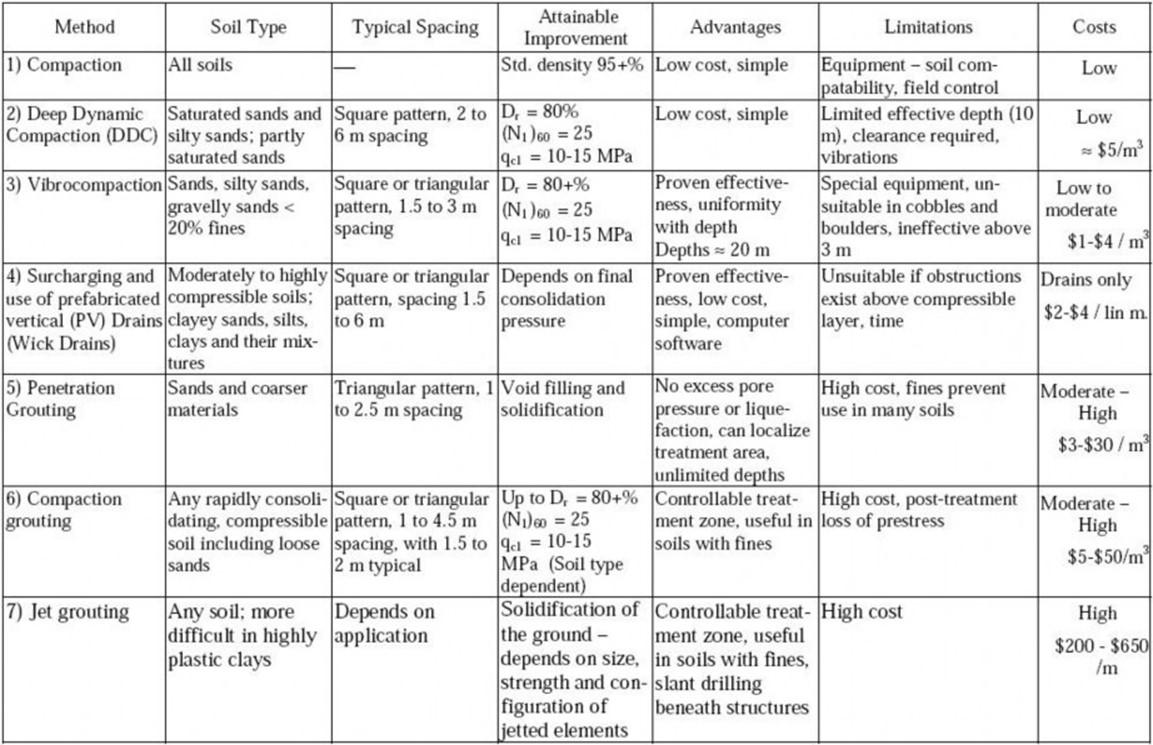
131
Reference: US corps of army engineers, 1999
Summary of ground improvement Methods
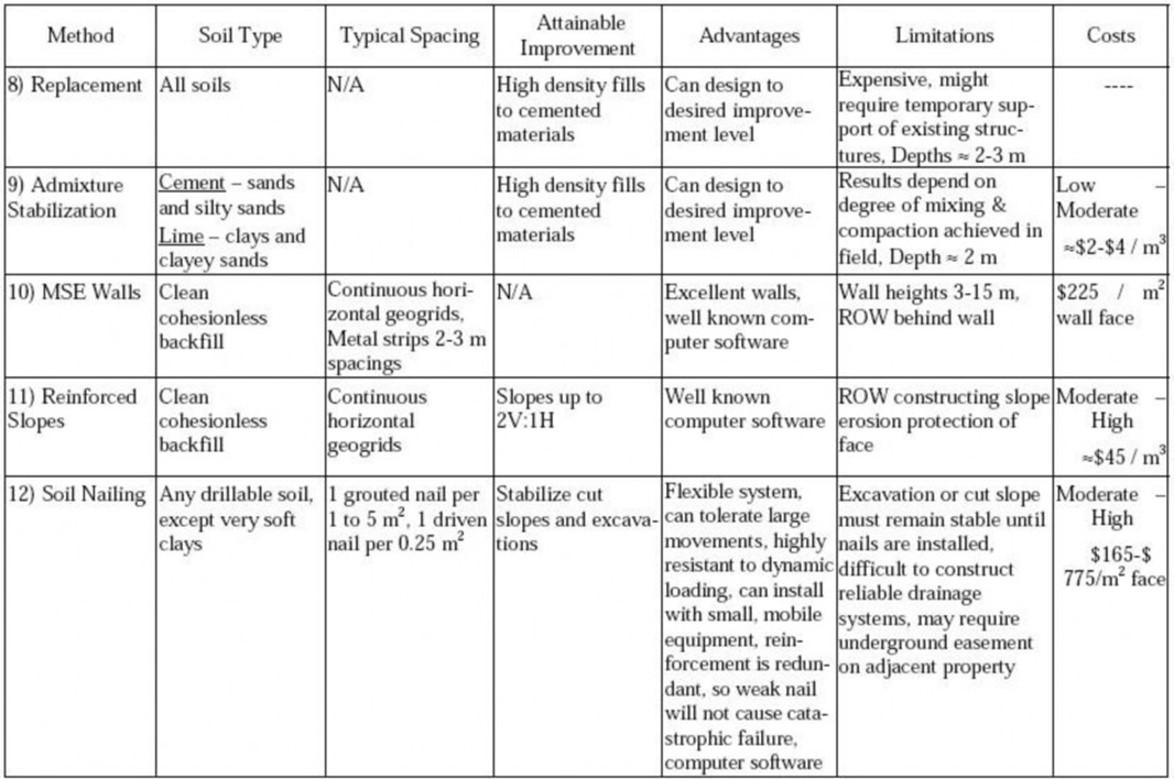
Summary of ground improvement Methods
Thank You