COMMON TYPES OF SURFACES
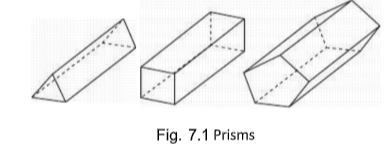
Prism
A prism is a polyhedron (shape with multiple faces) having identical and parallel bases
(or ends) connected by lateral laces which are parallelograms. The axis of a prism is a
straight line connecting the centers of the bases.
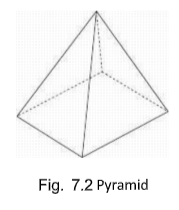
Pyramid
A pyramid is a polyhedron whose base is a polygonal plane and whose other surfaces are triangular planes converging to a single point called the VERTEX or the APEX. The axis is a line joining the apex and the center of the base. The altitude is the perpendicular distance from the apex to the base.
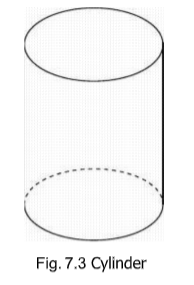
Cylinder
A cylinder is a single-curved surface generated by moving a straight-line generatrix
along a curved path/directrix such that the generatrix remains parallel to itself.
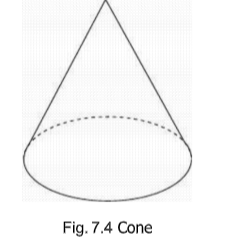
Cone
A cone is a single-curved surface generated by a straight line generatrix one end of
which remains fixed at a point called VERTEX of the cone while the other end moves
along a curved directrix called BASE of the cone. Axis of the cone is a line joining the
vertex and the center of the base.
Truncated Shape
A truncated shape is that portion of a geometric shape which lies between the base and
a cutting plane cutting all the elements.
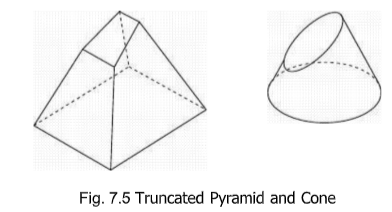
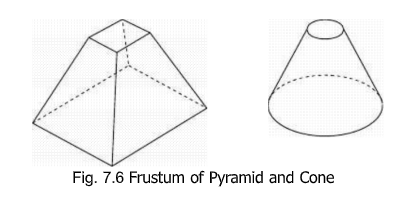
Frustum of a Shape
Frustum of a shape is that portion of the geometric shape which lies between the
base and a cutting plane parallel to the base cutting all the elements.

Right Shape
If the axis of a shape is perpendicular to its base, then that geometric shape is
termed as a right shape. Examples are a right cone and a right pyramid as shown in the
above figures.