Paints and varnishes
Paints
Paints are used to protect metals, timber, or plastered surfaces from the corrosive effects of weather, heat, moisture or gases etc and to improve their appearance.
Fundamental components of an oil-based paint are:
- Body
- Vehicle
- Pigment
- Thinner
-
Dryer
Body or Bases
Makes the paint film harder and more resistant to abrasion
Commonly used bases (body) are White lead, Zinc oxide, Iron oxide, Metallic powder such as Al, Cu, Br.
The binder or resin, is the actual film forming component of paint.
Dryers
Added to quicken the drying of vehicle
Vehicle
Oily liquid in which the body and pigment are soluble
Facilitates the paint to be conveniently spread over the surface
Oils most commonly used as vehicle.
Pigment
Pigments are materials which gives the paint its color.
Thinner
Liquid thinner is added in the paint to Increases fluidity
Common Defects in painting
Fading:
-
The gradual loss of color is known as fading. This may be due to the effect of sun rays.
Flaking or Peeling
-
Due to the poor adhesion, paint may peel off from the surface.
Blistering:
- This is caused by water vapour, which is trapped behind the painted surface. It may occur due to imperfect seasoning of timber.
-
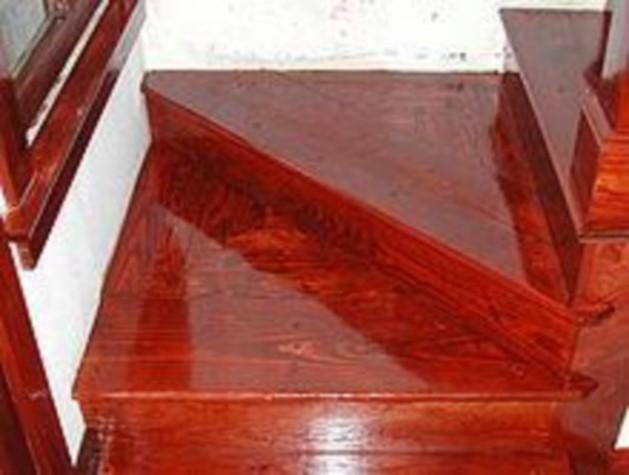
VARNISH
A transparent solution of resinous substance in linseed oil, turpentine or in alcohol is called varnish.
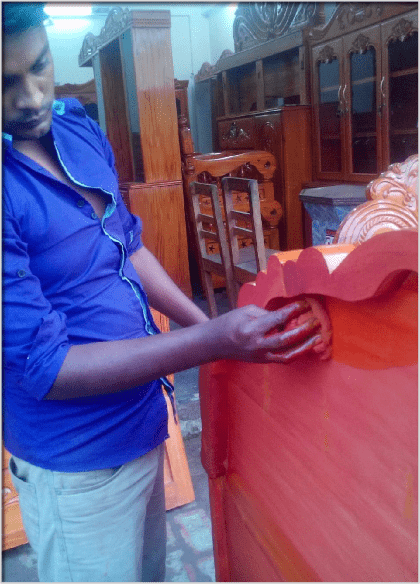


Painting the woodwork – Steps
-
Preparation of surface:
Use Seasoned wood, press nails gently before painting.
-
Knotting:
The knots covered with suitable material is called knotting.
-
First coat:
After knotting the primary coat is applied on the surface of the wood. It is usually applied before the wood work is fixed.
-
Second coat:
This coat is applied after knotting and priming coat. Each coat applied longitudinally in thin film and crossed, so that no brush mark is seen on this painted surface.
- Final coat:
This coat is applied over the second coat without any brush mark.