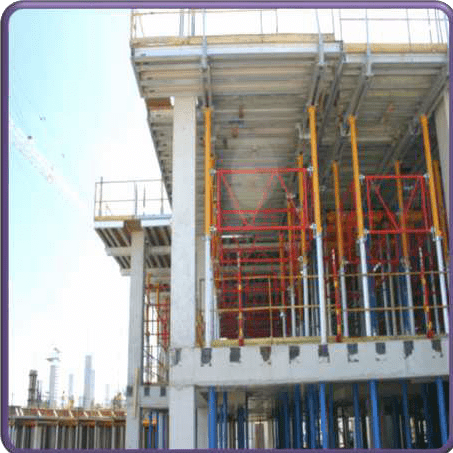
FORMWORK
What is Formwork?
-
Formwork is a mould including all supporting structures, used to shape and support the concrete until it attains sufficient strength to carry its own weight.

-
It should be capable of carrying all imposed dead and live loads apart from its own weight.
Formwork is commonly made of
- Steel
- Timber
- Steel
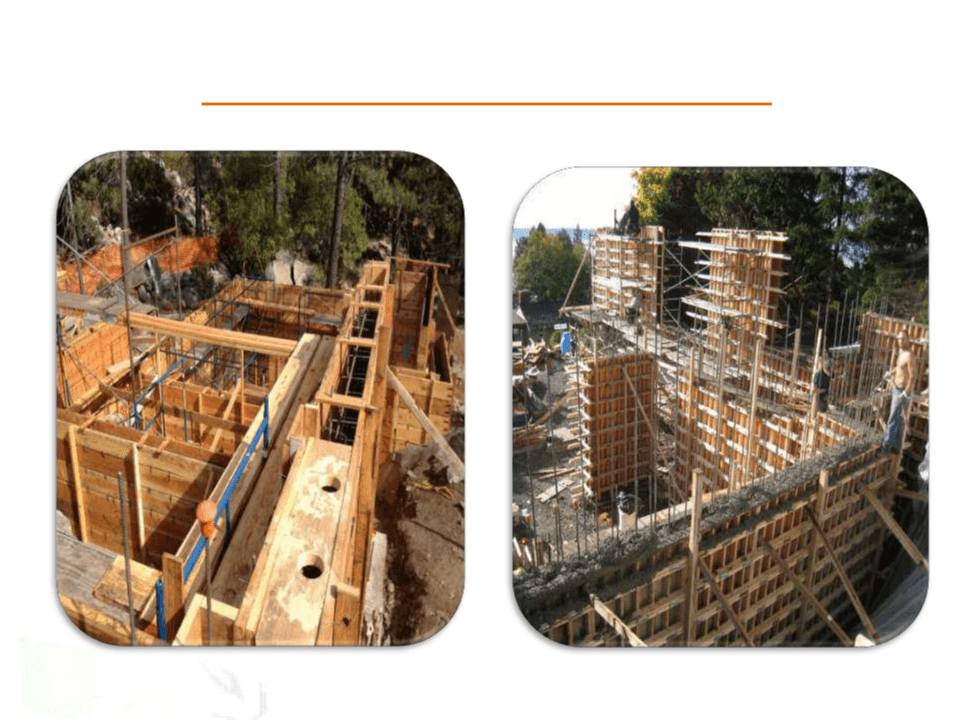
TIMBER FORMWORK

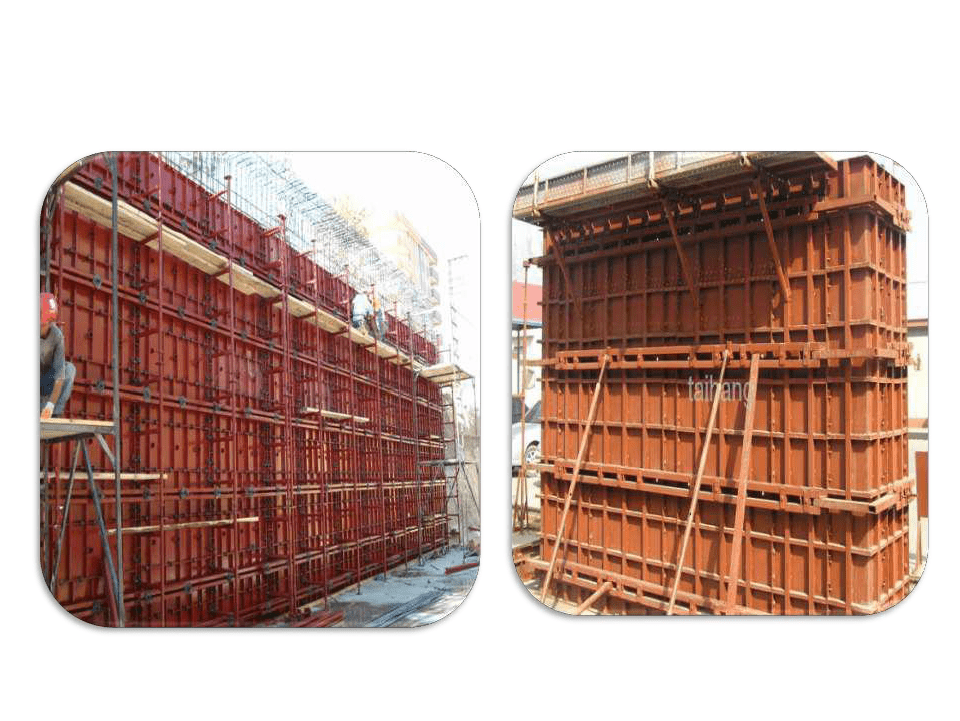
STEEL FORMWORK
- Formwork has been in use since the beginning of concrete construction.
- New materials such as steel, plastics and fibreglass are used in formwork.
- Greater attention is being given to the design, fabrication, erection and dismantling of formwork
- Formwork is designed according to The ACI document SP-4.
Qualities of Formwork

- It should be water tight.
- It should be strong.
- It can be reusable.
- Its contact surface should be uniform.
- It should be according to the size of member.
-
In order to successfully carry out its function, formwork must achieve a balance of following requirements:
- Containment
- Strength
- Resistance To Leakage
- Accuracy
- Ease Of Handling
- Finish And Reuse Potential
- Access For Concrete
- Economy
- Containment
-
Containment: formwork must be capable of shaping and supporting the fluid concrete until it cures.

-
Strength: formwork must be capable of safely withstanding without distortion or danger the dead weight of the fluid concrete is placed on it, labour weight, equipment weight and any environmental loadings.
-
Ease of Handling: form panels and units should be designed so that their maximum size does not exceed that which can be easily handled by hand or mechanical means.

-
In addition all formwork must also be designed and constructed to include facilities for adjustments, levelling, easing and striking without damage to the form work or concrete.
-
-
Economy: all the formwork is very expensive. On average about 35% of the total cost of any finished concrete unit or element can be attributed to its formwork; of this just over 40% can be taken for material for formwork and 60% for labour.
-
The formwork designer must therefore not only consider the maximum number of times that any form can be reused, but also produce a design that will minimize the time taken for erection and striking.

-
-
Major objectives considered in formwork:
Quality
Safety
Economy
-
Quality:
Forms must be designed and built with sufficient stiffness and accuracy so that the size, shape, position, and finish of the cast concrete are maintained.
-
Safety:
Forms must be built sufficient strength and factor of safety the capable of all supporting loads.
-
Economy:
Forms must be built efficiently, minimizing time and cost.
so that they have
Requirements of formwork:

- Material should be cheap and re usable,
- It should be practically water proof, so that it should not absorb water from concrete,
- Swelling and shrinkage should be minimum,
- Strong enough to with stand all external loads,
- Deflection should be minimum,
- Surface should be smooth
- Light in weight, so that easy to transfer,
- Joints should be stiff, so that lateral deformation and leak
- Material should be cheap and re usable,
is minimum .

Three stages in the process :
-
Assembly and erection .

-
Concrete placement.
-
Stripping and dismantling.
-
Formwork detail for different
structural members
In concrete construction formwork is commonly provided for the following structural members.

- Wall
- Column
- Slabs & Beams
- Stairs
- Chimneys
-
Water tanks
-
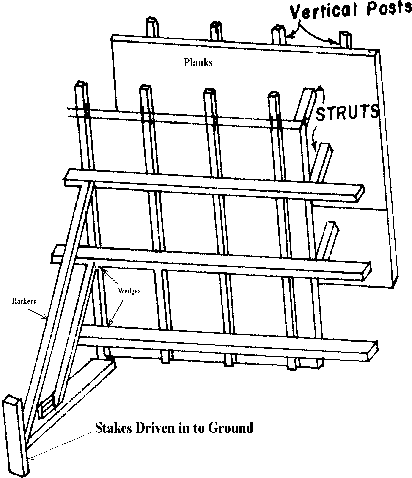
Formwork for Wall
-
It consists of
- Timber sheeting
- Vertical posts
- Horizontal members
-
Rackers
- Timber sheeting
- After completing one side of formwork reinforcement is provided at the place then the second side formwork is provided.
-
-
- Wall
-
Formwork for Column
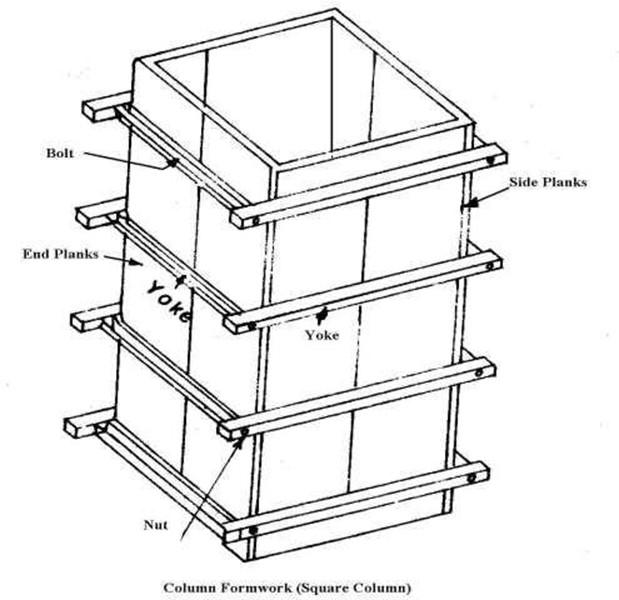
-
It consists of the following
- Side & End Planks
- Yoke
- Nut & Bolts
- Side & End Planks
-
Two end & two side planks are joined by the yokes and bolts.
- Formwork for columns



-
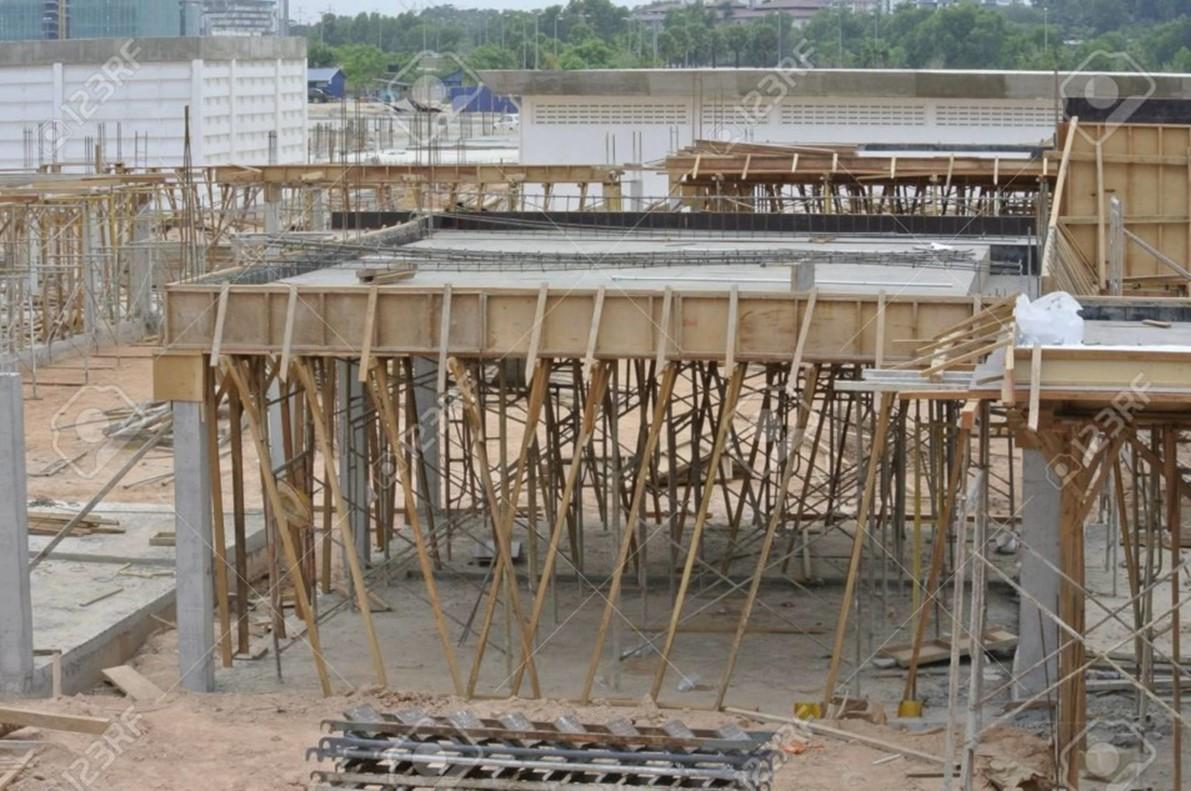
Formwork for Slabs & beams•:

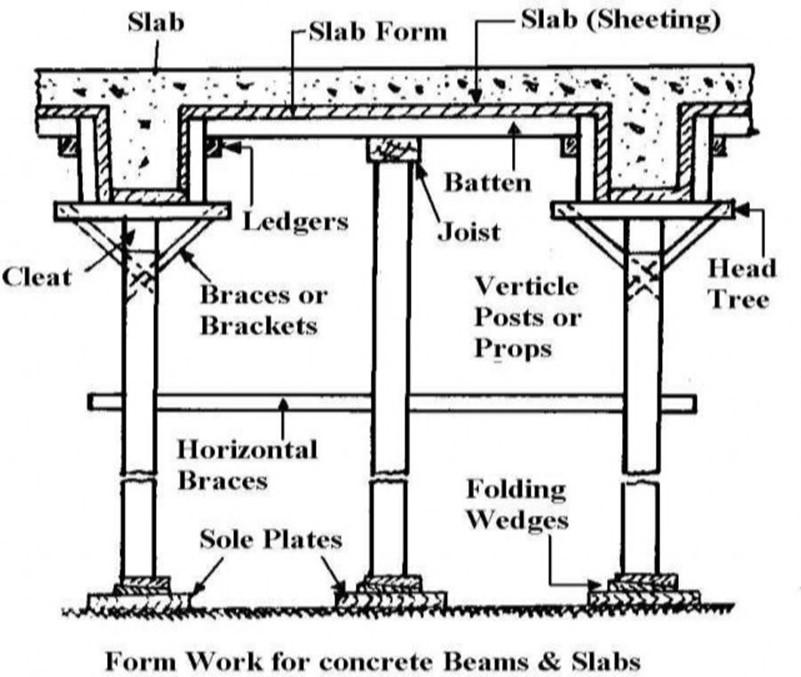
It consists of
- Sole plates
- Wedges
- Props
- Head tree
- Planks
- Batten
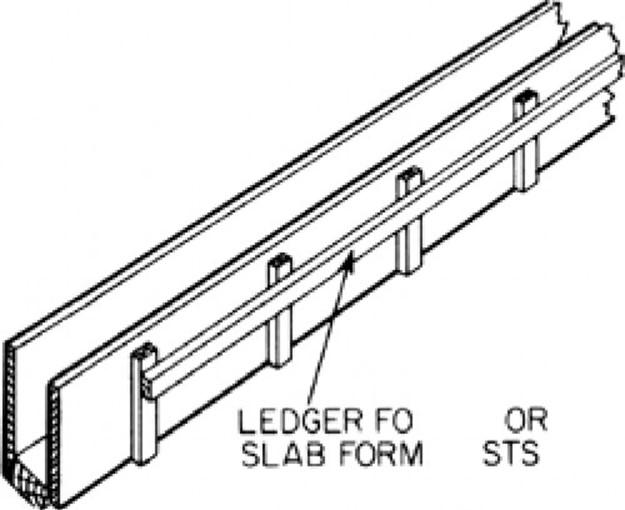
-
Ledgers
- Beam formwork rests on head tree
-
Slab form work rests on
battens and joists
- If prop height are more than 8′ provide horizontal braces.
- Beam formwork rests on head tree
- Sole plates
-
-
FORMWORK FOR SLAB:
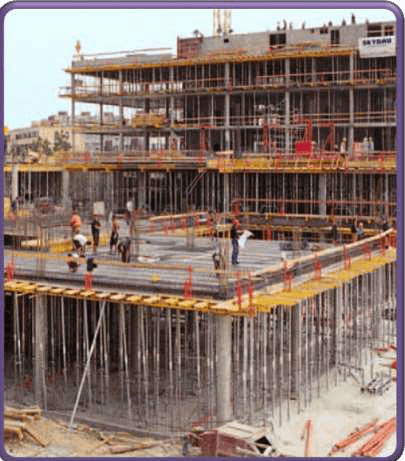


-
FORMWORK FOR STAIRS:
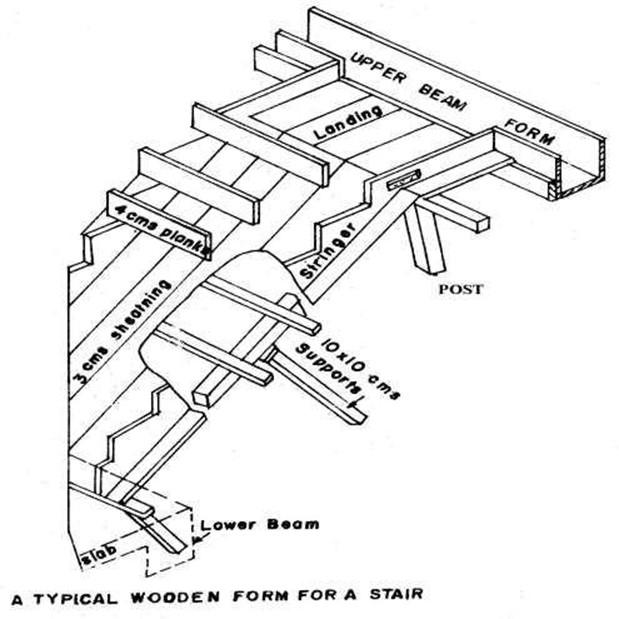
-
It consists of
- Vertical & inclined posts
-
Inclined members
— Wooden Planks or sheeting
- Stringer
- Riser Planks
- Vertical & inclined posts
- FORMWORK FOR STAIRS:
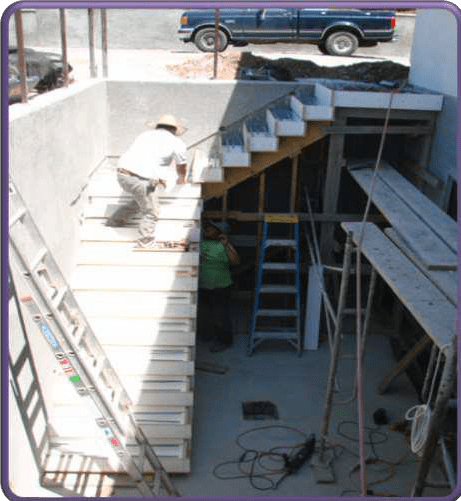

-
-
-
FORMWORK FOR SPIRAL STAIRS :
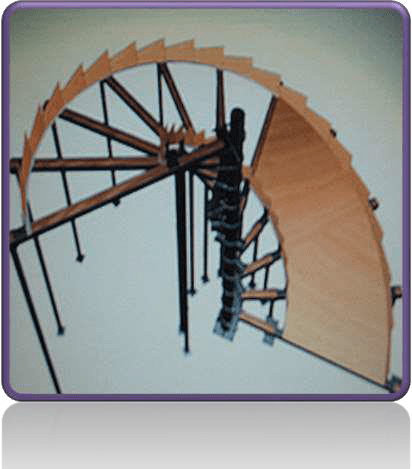


-
FORMWORK FOR CHIMNEYS:
For tall chimneys two types of forms techniques are in generally use in our country

- Jump form
- Slip form
- Jump form
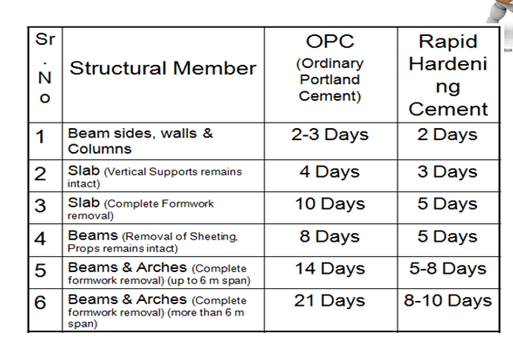
- Removal of formwork:
- Time of formwork removal depends on the following factors
-
Type of Cement
- Rapid hardening cements require lesser time as compared to OPC (Ordinary Portland Cement)
-
Ratio of concrete mix
- Rich ratio concrete gain strength earlier as compared to weak ratio concrete.
- Rich ratio concrete gain strength earlier as compared to weak ratio concrete.
-
Weather condition
- Hydration process accelerates in hot weather conditions as compared to cold and humid weather conditions.
- Hydration process accelerates in hot weather conditions as compared to cold and humid weather conditions.
- Rapid hardening cements require lesser time as compared to OPC (Ordinary Portland Cement)
Time of Removal of formwork:
Cantilever slab
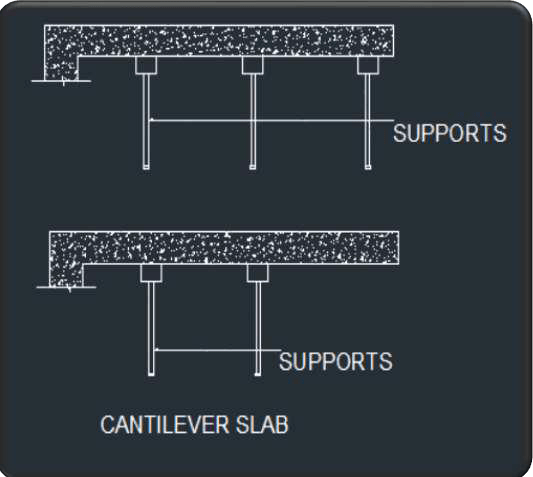
-
First free end’s support should be removed.
-
And then from right to left it
should be proceed.
-
If we are removing from the mid span then it will act as a prop cantilever.
Simply supported slab
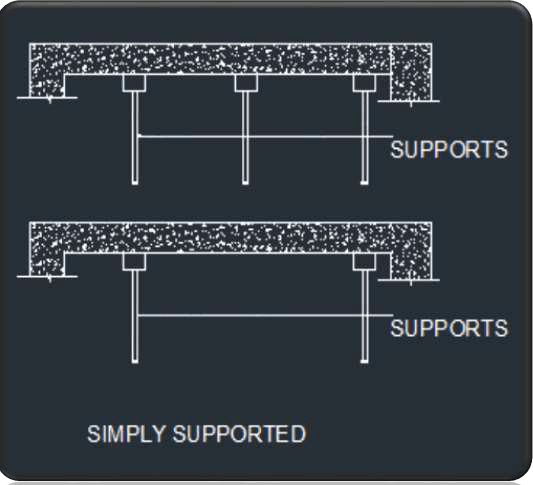
-
In simply supported we
have to remove the support from the mid span to the ends.
- To meet the design behavior.
-
-
Maintenance of formwork:
- Due to continuous use wooden planks & steel plates surfaces become uneven and require maintenance.
- For wooden formwork use cardboard or plastic fiber board. Bolt hole places must also be repaired.
-
For steel formwork plates must be leveled by mallet and loose corners must be welded.
-
Cost of formwork
-
For normal works cost of formwork is about 30%-40%
of the concrete cost.
-
For special works cost of formwork is about 50%-60%
of the concrete cost.
-
Formwork cost is controlled by the following factors

- Formwork Material cost
- Formwork erecting cost
- Formwork removal cost
- Formwork jointing cost (Nails and Cables)
- Labor charges.
- Formwork Material cost
-
-
- Due to continuous use wooden planks & steel plates surfaces become uneven and require maintenance.
-
Advantages of steel form work:
- It can be used for a no. of times.
- It is non absorbent.
- Smooth finish surface obtained.
- No shrinkage of formwork occurs.
- Easy to use.
- Its volume is less
- Its strength is more.
- LOADS ON FORMWORK:
- It can be used for a no. of times.
-
Dead load
- Self weight of formwork
- Pressure and loads from fresh concrete
- Reinforcement
- Self weight of formwork
-
Imposed load
-
Construction workers

- Stacking of materials
-
- Horizontal loads
-
Environmental loads
- Accidental loads
- Wind loads
- Accidental loads

Thank you
THANK YOU