Materials and Method of Construction
(Introduction)
Engineering Materials
-
There are thousands of materials available to the engineer !
-
Basic construction materials: concrete, steel, clay products & Wood etc.
Course Objectives
-
To develop a basic understanding of key material properties, requirements, and related behavior characteristics of typical construction materials.
-
- Types
- Production methods
-
Uses in construction
- Building Stones
- Metals
- Clay Products
- Lime
- Cements
- Aggregates
- Concrete
- Glass
- Paints and Varnishes
- Building Stones
- Properties of the following materials of construction:
-
These materials are used in all civil engineering structures such as;
- buildings
- bridges
- highways
- railways
- tunnels
- dams
- towers etc.
- buildings
Books
-
Fundamentals of Building Construction Materials and Methods by Edward Allen and Joseph Iano 5th Edition
-
Building Materials by S.K Dughal 3rd Edition
-
Building Construction (Principals, Materials and System) by Madan Mehta 2nd Edtion
CLASSIFICATION OF CIVIL ENGINEERING MATERIALS
-
According to their phases
- According to their internal structure & chemical composition
Phase Classification
- Gases : Air, oxygen, CO2
-
Liquids : Water, chemical admixtures
-
Semi-solids : Fresh pastes, mortars, asphalt
-
Solids : Metals, hardened concrete
Internal Structure & Chemical Composition Classification
-
Metals : (formed by metallic bonds)
-
Ferrous (iron, cast iron, steel)
-
Non-ferrous (aluminum, copper, zinc, lead)
-
-
Polymers : (long chains having molecules of C, H, O, N which are formed by covalent bonding.)
- Natural (rubber, asphalt, resins, wood)
-
Artificial (plastics)
Natural
Rubber

Natural
Resins


Natural Asphalt

Internal Structure & Chemical Composition Classification
- Natural (rubber, asphalt, resins, wood)
-
Ceramics :
- Structural clay products (bricks, tiles, pipes)
-
Porcelains((
نترب ےک یٹم ینیچ ) is a ceramic
material made by heating materials, generally including kaolin(china clay), in a kiln to temperatures between 1,200 and 1,400 °C)
- Structural clay products (bricks, tiles, pipes)
-
Composite Materials :
(Portland cement concrete)

- Reinforced Composite Materials :
-
(reinforced concrete, reinforced plastics)

- One of the most important tasks of an engineer is to select the most suitable material for a given civil engineering structure.
Factors Factors Determining the Choice of Proper Material for a Structure
-
Economy. Choose the cheaper & available materials considering
- Initial cost
- Useful life
- Frequency of maintenance
- Cost of maintenance
- Salvage value etc.
- Initial cost
Example: Comparison of Concrete Pavement vs. Asphalt Pavement for economy.
ConcreteAsphaltInitial Cost– (More)+ (Less)Useful Life+(Long life)–(short)Frequency of Repair+(Less)–(More)Cost of Repair–(More)+(Less)Salvage Value-(Less)-(Less)General Properties of Civil Engineering Materials
Physical **
- Mechanical **
- Chemical
- Other
– Thermal, Acoustical, Optical, Electrical
** Most CE Applications focus on physical & mechanical properties
Physical Properties
-
Properties of physical structure
-
Density (mass/volume)
-
Specific gravity(ratio of the density of a substance to the density of water – at a specified temperature(4oC)).
-
Porosity (Porosity or void fraction is a measure of the void (i.e. “empty”) spaces in a material, and is a fraction of the volume of voids over the total volume, as a percentage between 0 and 100%.)
Physical Properties
Property of a material that lets fluids (such as water or water vapor) to diffuse through it to another medium without being chemically or physically affected.
Mechanical Properties
-
Resistance to applied loads (stress) initially & over time
-
Stiffness
Stiffness is the rigidity of an object — the extent to which it resists deformation in response to an applied force
-
Strength
The capacity of an object to withstand maximum force.
- Fracture (brittle)
- Yielding (ductile)
- Fracture (brittle)
-
-
-
Mechanical Properties
- Tension
-
Compression
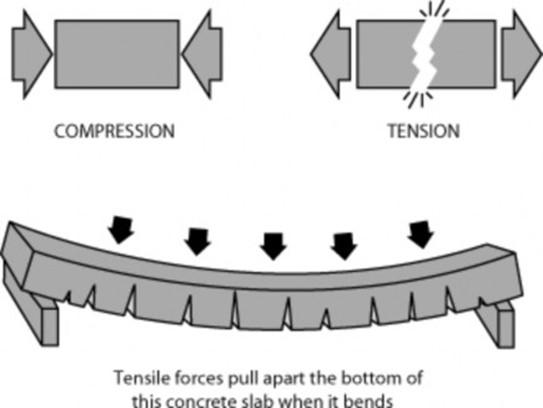
- Flexure
- Torsion
Determining the Properties of Civil Engineering Materials
-
Properties of materials are determined by
- Laboratory testing
- Field testing
- Laboratory testing
-
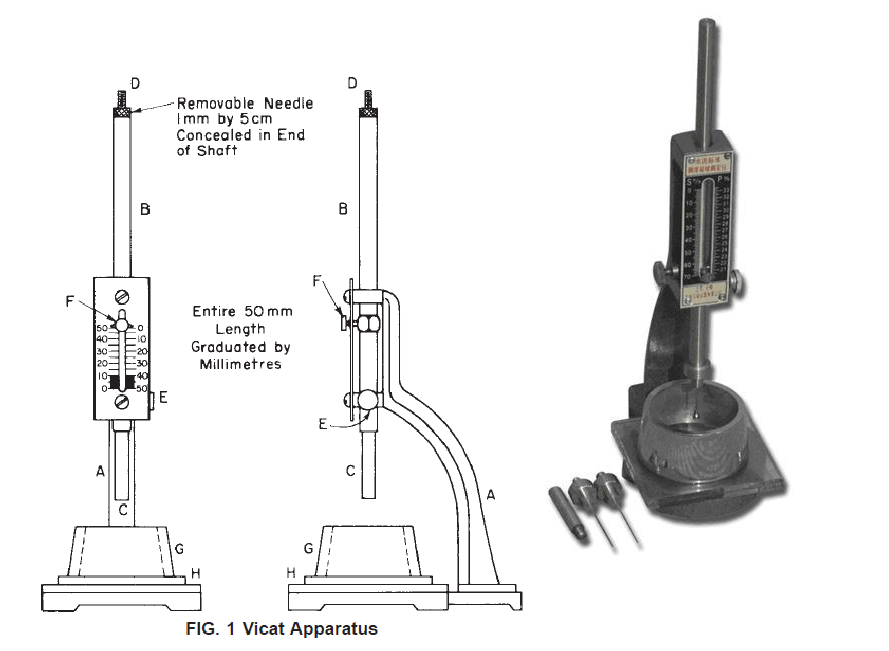
To avoid inconsistencies in test results STANDARDS are devised which describe the test apparatus and the procedure.
Items that are usually standardized in a test are:
Items that are usually
standardized in a test are:
- Obtaining test specimens and number of specimens
- Size and shape of the specimen
- Preparation of specimens for testing
- Temperature & moisture during preparation & testing
- Type of machinery
- Rate of loading
- Interpretation of test results
-
Writing a report
Standardization Institutes
- Turkey – Turkish Standards Institute (TSE)
- England – British Standards Institute (BSI)
- Germany – Deutsche Institute Norm (DIN)
- U.S. – American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM)
- Europe – European Committee for Standardization (CEN)
-
India – Indian Standard (IS)
(ASTM)

(ASTM)
CEMENTITIOUS MATERIALS
- Turkey – Turkish Standards Institute (TSE)
- Obtaining test specimens and number of specimens
-
Although there are several different materials which have adhesive properties, three types are of particular interest to civil engineers.
- Glues : materials of gelatinous nature derived from vegetable or animal sources.
- Bituminous Materials : complex hydrocarbon
- Various Compounds of Calcium : gypsum, lime, cements
- Glues : materials of gelatinous nature derived from vegetable or animal sources.
-
Cementitious materials are substances which, upon certain chemical reactions attain binding properties
-
Non-hydraulic cements (gypsum and lime)
-
Hydraulic cements (portland cement)
-
-
Hydraulicity is that property of gaining binding value when mixed with water.
Bridges: Wood


Bridges: Masonry
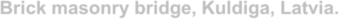

Stone arch bridge, Mérida, Spain.
1st century

Brick masonry bridge, Kuldiga, Latvia. Originally completed in 1874, destroyed in 1915, rebuilt in 1926.
Bridges: Steel

Luis I bridge, Porto, Portugal.


Howrah bridge, Kolkata. Completed in 1943, replaced a floating bridge of 1874.
Completed in 1886.

Bridges: Steel
Golden Gate bridge, San Francisco, USA.
Completed in 1937.


Sydney Harbour bridge, Sydney, Australia.
Completed in 1932.


Bridges: Concrete


Confederation bridge, Canada.
Completed in 1997.

Bridges: Concrete

Great Belt Link bridge, Denmark/Sweden.
Completed in 1998.

Millau viaduct, France.
Completed in 2004.


Options in Construction
Bridges: Composites
Kings Stormwater Channel bridge, California, USA.
Completed in 2001.



Buildings: Wood


Tamilnadu.
17th century.

Options in Construction
Buildings: Brick Masonry

USA

Options in Construction
Buildings: Stone Masonry



Qutab Minar, Delhi.
Completed in 1230.
Cologne Cathedral, Cologne, Germany
1248-1880, damaged during WW II, repaired.

Options in Construction
Buildings: Wood and Masonry

Bourges, France.

Liuheta pagoda, Hangzhou, China
Present form dates to 1152.
15th century.
Options in Construction
Buildings: Concrete
Marina City, Chicago, USA.
1959


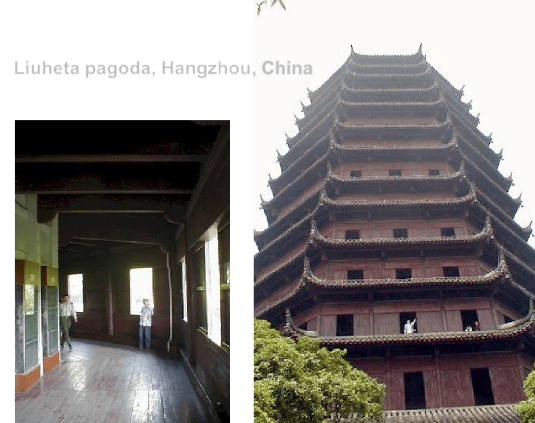
Petronas Towers, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
Completed in 1998.
Options in Construction
Buildings: Steel Framed
Taipei 101, Taipei, Taiwan
Completed in 2004.



Sears Tower, Chicago, USA.
1973

Options in Construction
Buildings: Glass and Steel



GLA Building, London, UK.
2002
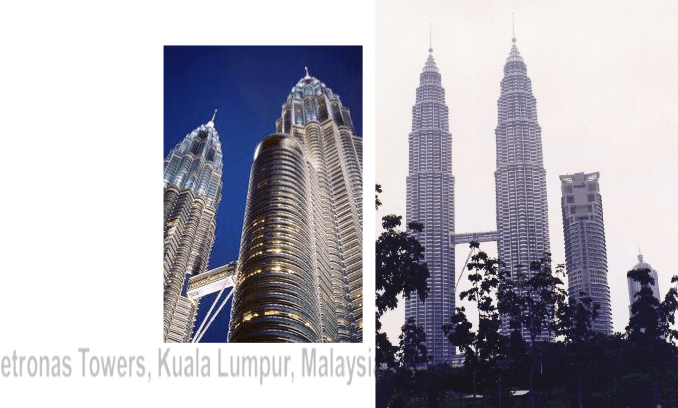
Apple Computer Store, Soho, New York, USA.
Completed in 2002.

Options in Construction
Buildings: Titanium-clad Steel and Limestone
Guggenhiem Museum, Bilbao, Spain.
1997




- Type of application
- Cost-effectiveness
- Availability (geographical location)
- Climate
- Performance requirements
- Aesthetics
- Environmental concerns
THANK YOU