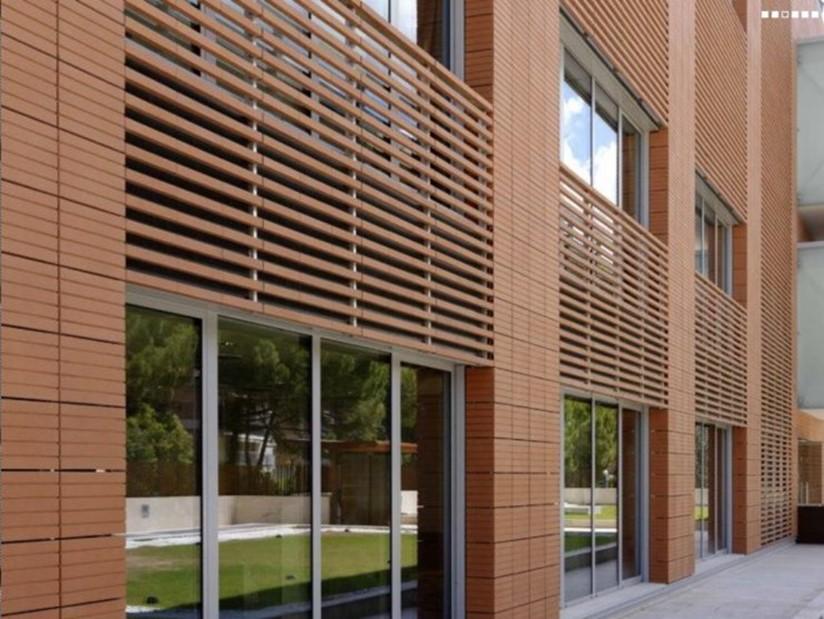
Ceramic Tiles
Materials and Method of Construction
Building Stones &
Ceramic Tiles
-
Rock :
A large concreted mass of earthy or mineral matter
-
Stone :
Quarried or smaller pieces of rock for a specified function such as a building block
GEOLOGICAL CLASSES OF ROCKS
-
Igneous: Formed by cooling and thus solidfying from a molten state. (Granite, Basalt)
-
Sedimentary : Formed by a process of cementation of small particles that result from the disintegration of rocks. (Limestone, sandstone)
-
Metamorphic Rocks : Formed by gradual changes in the structures of either igneous or sedimentary rocks caused by heat, water, pressure. (Marble, Slate)
Stone Masonry
Commercial Stone Types
- Granite
- Granite
For commercial purposes, building stone is classified into six groups according to ASTM C199.
- Limestone
- Quartz-based
- Slate
- Marble
- Other
COMMONLY USED BUILDING STONES
-
Granite :
- Intrusive igneous rock
- Granite is a strong, hard & non- porous rock
-
It is a desirable foundation & building material.
- Intrusive igneous rock
- Quartz Based:
- Sedimentary Sandstone: from quartz deposits
-
Brownstone, and some varieties of bluestone are varieties of sandstone

-
Limestone : Sedimentary rock
- It is used as a concrete aggregate
-
It is used in the production of cement & lime

- It is used as a concrete aggregate
-
Marble : Metamorphosed limestone
- Harder than limestone
-
Used for interior work or wall or column facing
- Harder than limestone
- Slate : Metamorphosed clay
-
- Used for flooring, interior or exterior wall facing.

Stone Masonry
Stone Selection
High density and low water absorption correlate with greater durability.
Stone Masonry
Stone Masonry
May also be dry set, stacked without mortar or set on shims with sealant-filled joints.
Stone Masonry
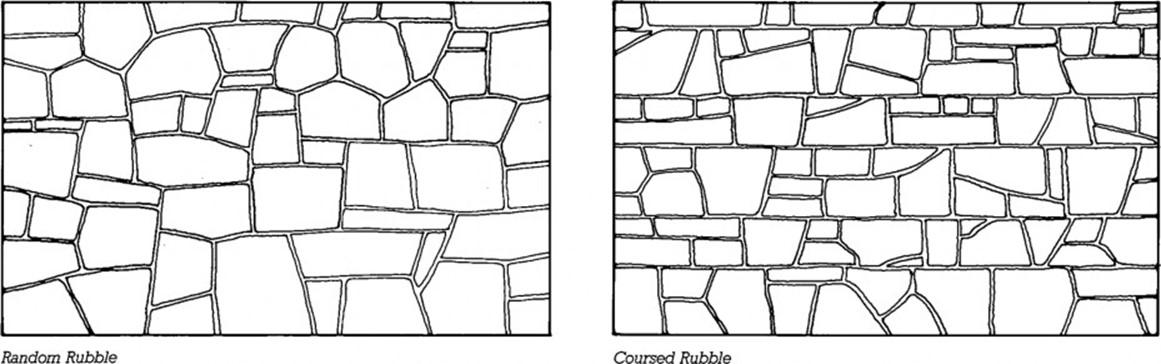
Rubble Masonry
Unsquared stone blocks
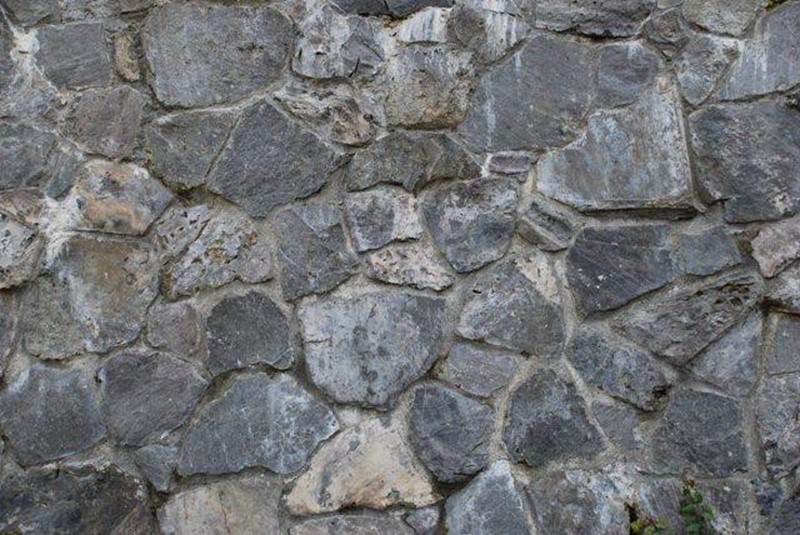

Stone Masonry
Rubble Masonry
Random: Laid without continuous horizontal joints
Coursed: Laid with continuous horizontal joints
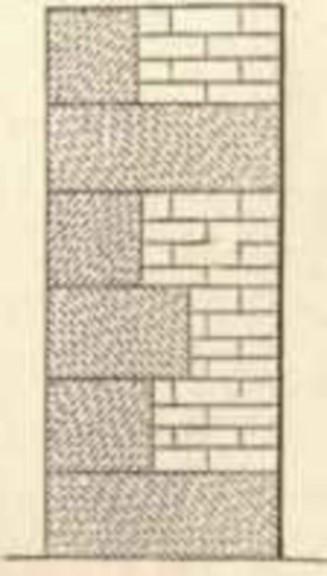
Stone Masonry
Ashlar Masonry
Squared blocks
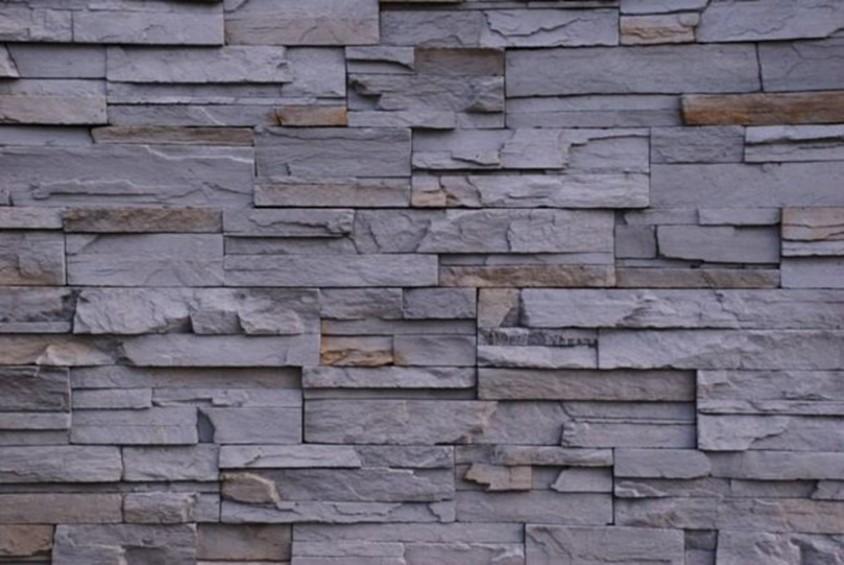

Ashlar Masonry
The various types of Ashlar masonry can be classified under the following categories are
- Ashlar fine
- Ashlar rough
- Ashlar rock or quarry faced
- Ashlar facing
- Ashlar chamfered
-
Ashlar block in course
Ashlar Masonry


Ashlar fine Ashlar rough
Ashlar Masonry

Ashlar rock or quarry faced
Ashlar facing
Ashlar Masonry
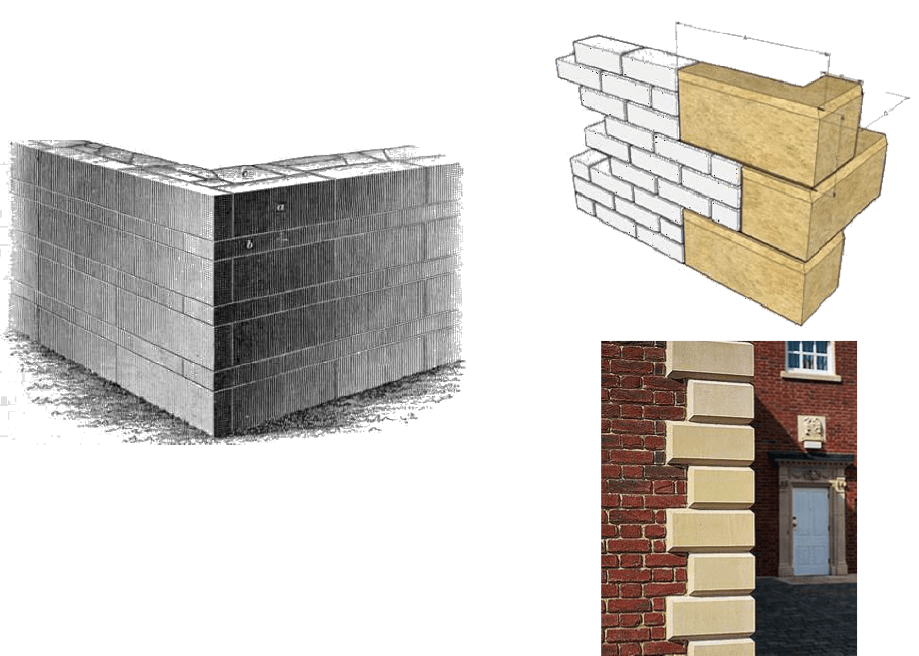
Ashlar block in course Ashlar chamfered
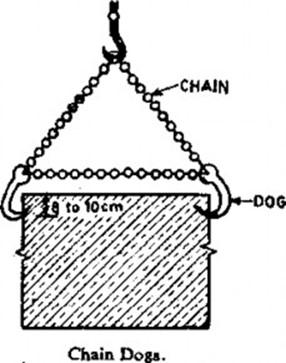
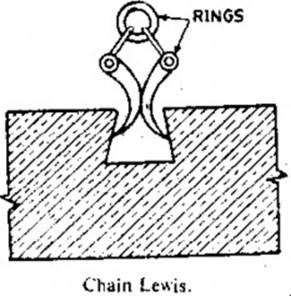
Lifting Appliances for Stone Masonry
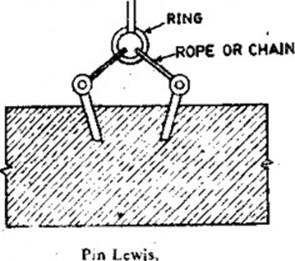
- Pin Lewis
- Chain Dogs
- Chain Lewis
- Three Legged Lewis
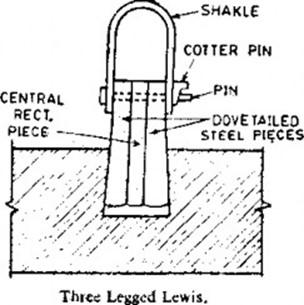
PRODUCTION STEPS
-
Quarrying: Big chunks are cut at the side, loosened at the bottom by wedging & removed by cranes
- Shaping & Finishing: Taken to the factory & cut and finished to the desired shapes.


PROPERTIES OF STONES
- Durability : mainly abrasion
- Strength
- Both strength & durability are affected by the texture & mineral composition, chemical charactersitics & physical characteristics.
- Porosity
- Water Absorption
- Coefficient of thermal expansion
-
Fire resistance
Uses of Stones
-
Building foundations, walls, piers, pillars, and architectural
works.
- Lintels, Beams, beams Arches, domes etc.,
- Cladding Works
- Dams, light houses, monumental structures.
- Paving jobs
-
Railway, ballast, black boards and electrical switch boards
-
Pakistan Stone Development Company
Ceramic Tiles: The Basics
- Ceramic means “fired clay” and tile means “covering.”
- Common raw materials are sand, clay, talc, feldspar.
- A ceramic tile is just clay that’s formed, glazed and baked.
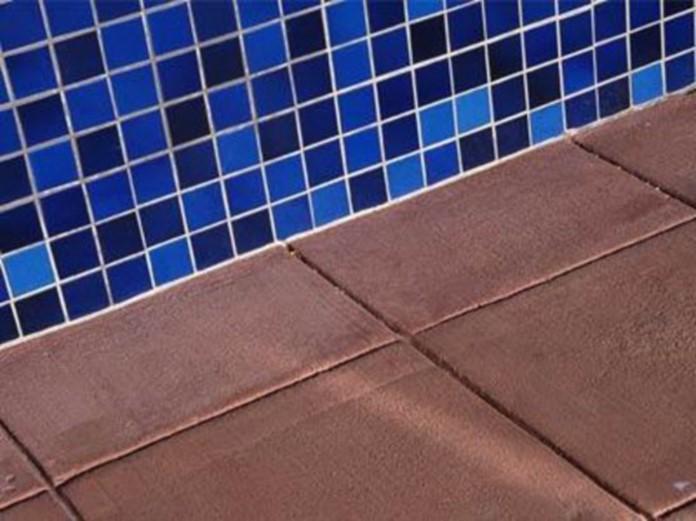

Figure: Wall & floor tiles.
Tile, Ceramic (clay) – Glazed
- Glazed (fired) in a high temperature kiln
- Stone Look -slate or other finishes
- Metallic Glazed (fired)
- Colors, textures, shapes are in the thousands
Tile, Ceramic (clay) – Unglazed
Clay body – Fired – Not glazed or coated
- Mexican Tile – Saltillo(In the family of terracotta tile, but more rustic)
- Mosaic Tile (Small – square, hex, rectangle)
-
Porcelain Tile (Stone Look” has stone texture and colors pressed into the face)


- Quarry Tile(Top is a wood pattern quarry tile)
- Terracotta Tile

Terra cotta cladding
Other Types of Masonry



Site Selection
-
It means selection of best site for the project which provide
- Safety
- Economy
- Safety
- It is a project specific job.
-
It depends on the
- Requirements of user/client
- Use of Project
- Finance available
General Rules for site selection
- Requirements of user/client
- It should provide minimum disturbance to the residents of the area.
- Site should be selected that it provides good drainage.
- Site should be easily accessible.
- Construction material should be easily available.
-
Transportation of construction material is easy.
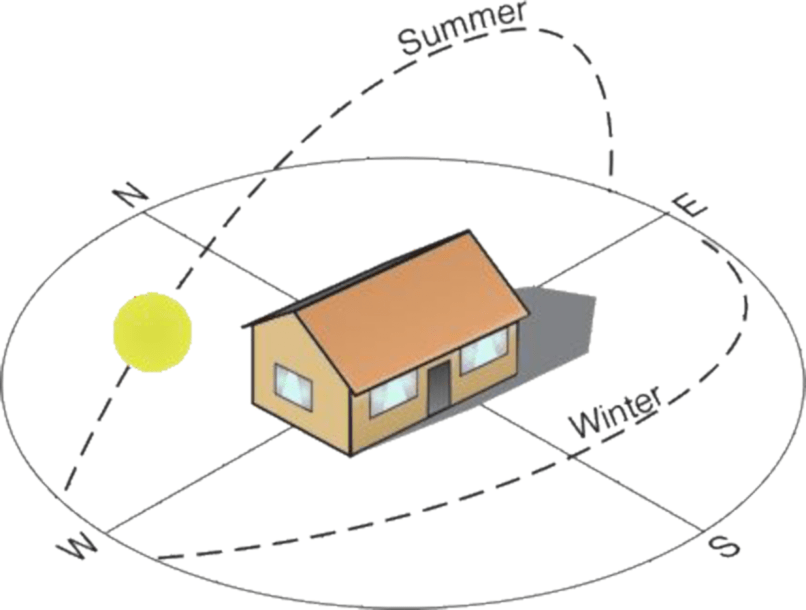
Orientation of Buildings & setting out of Civil engineering Projects
What is Orientation of buildings?
It is defined as the art of placing a building in such a position that its front faces a particular direction.
Object of Orientation of Buildings
To place the building so as to suit its surroundings. To provide natural comfort to users.
To provide privacy to inmates.
To protect residents from dust and noise pollution.
To place the building in such direction that its minimum portion comes in contact with direct rain showers so as to avoid dampness in building.
Factors effecting Orientation of Buildings
Following factors are important for deciding the Orientation of Buildings.
-
Surroundings of the Site
The building should be so oriented that it suits surrounding of the site.
-
Approach to road or street
Approach to nearby road means a good orientation.
- Sun Movement.
Sun path and sun rays are important in deciding the placement of different rooms in a building.
Sun Movement.
-
- Sun is the important source of energy, natural light and Temperature.
- If sunrays are properly falling on the building then it will provide a good living conditions in the buildings.
Arrangement of Different rooms in a Residential Building w.r.t Sun Movement
|
SE SE |
W SW |
|
SE |
NW |
|
S |
W |
|
NE |
SE |
|
NE |
NW |
N
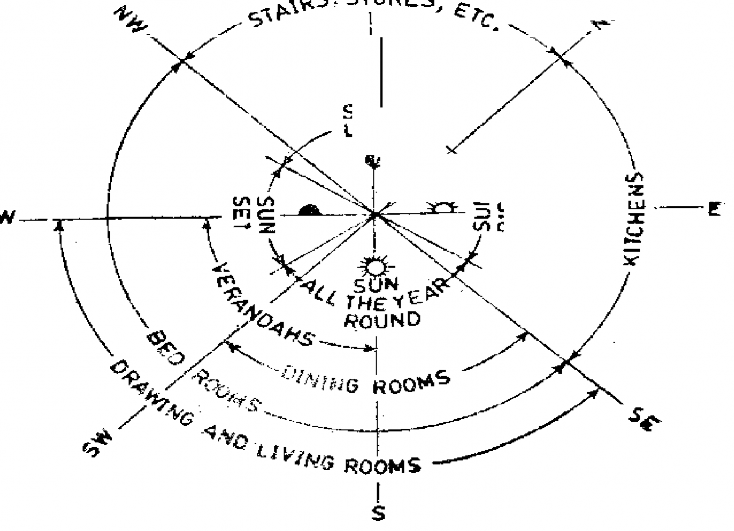
Pig. J..2. Method of placing: R.00.ms of a ResidcntiaJ .J3u ild jq w r ..t ..
tht.:: / J i :- ti o n ot’Sun.