Design Principles of Concrete Structures
Lecture 15
Two way slab design
Two-Way Edge Supported Slabs
Two-Way Slabs
Slab resting on walls or sufficiently deep and rigid beams on all sides. Other options are column supported slab e.g. Flat slab, waffle slab.
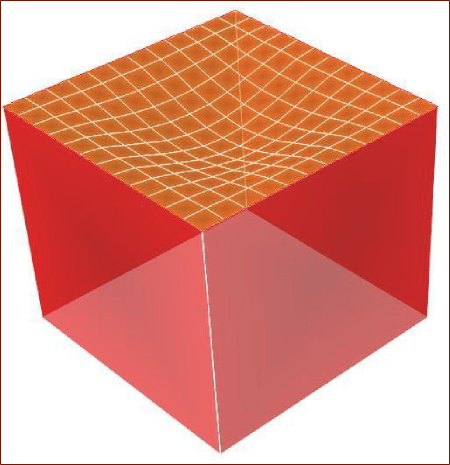
Isolated Two Way Slab
Design Methods
- ACI co-efficient method
- Direct design method
- Equivalent frame method
- Finite element method
Notes
-
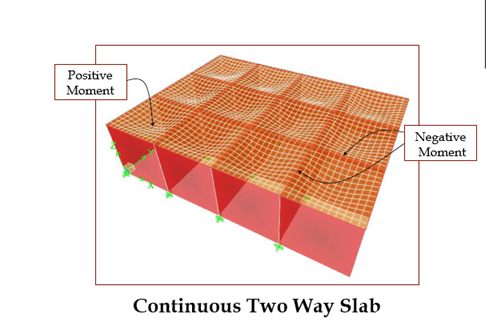
In two-way slabs shorter direction strip carry greater
%age of load.
- Steel will be more in shorter direction.
- Shorter direction steel will be placed near the outer edge to get more “d” means more lever arm to get more flexural capacity.
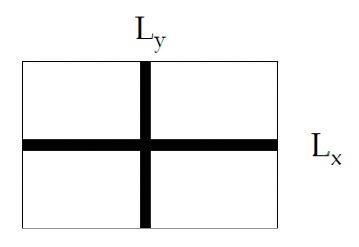
ACI Co-efficient Method
Unit width strip is taken in both directions. The strip is
designed separately for +ve and –ve moment.
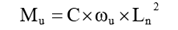
C = ACI co-efficient
ωu = Slab load
“C” depends upon the end conditions of slab and the aspect ratio.
Three tables are available for “C”
- Dead load positive moment
- Live load positive moment
- -ve moment
M+ coefficients are increased by 25 % and M– coefficients are reduced by 10 % to get the result more closer to accurate solution.
Minimum Depth of 2-Way Slab for Deflection
Control
According to ACI-318
hmin = (inner perimeter of slab panel)/180
≥ 90 mm
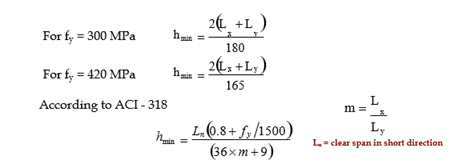
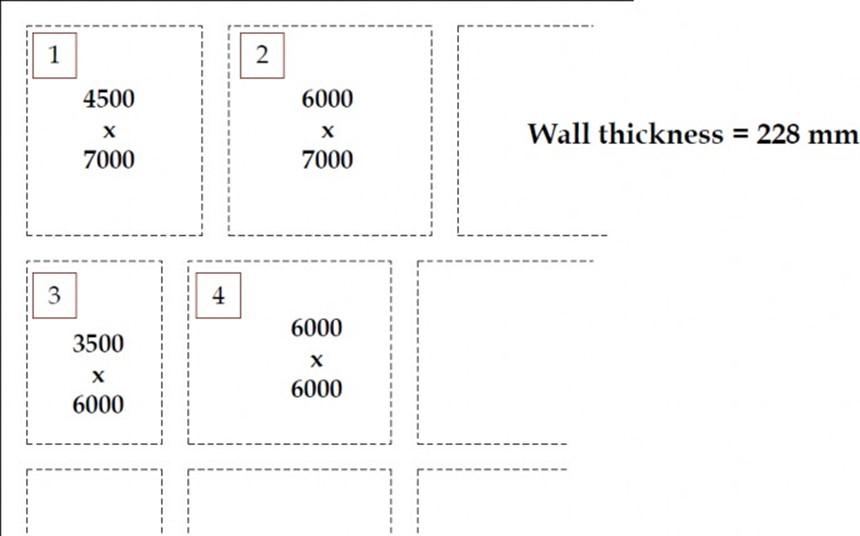
Example: Design the 4 marked slab panels of an ordinary house. Use US customary bars. fc’= 17.25 MPa fy = 300 MPa

Solution: Panel Edge Conditions
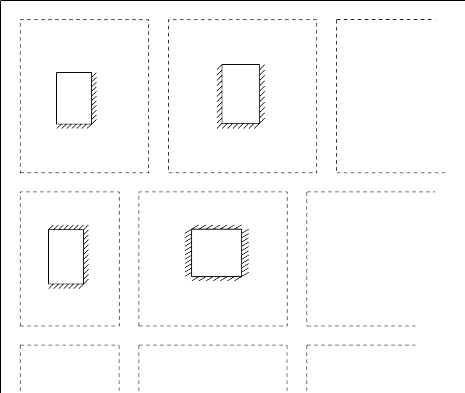
Panel # 1
Lx = 4.5m , Ly = 7.0m
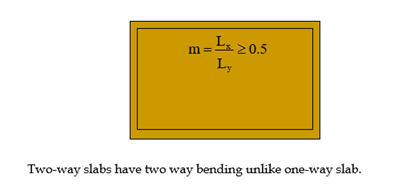
m = 0.64 > 0.5, 2-way slab
Panel # 2
Lx = 6.0m , Ly = 7.0m
m = 0.86> 0.5, 2-way slab
Panel # 3
Lx = 3.5m , Ly = 6.0m
m = 0.58 > 0.5, 2-way slab
Panel # 4
Lx = 6.0m , Ly = 6.0m
m = 1 > 0.5, 2-way slab
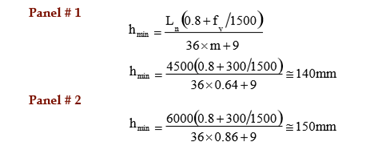
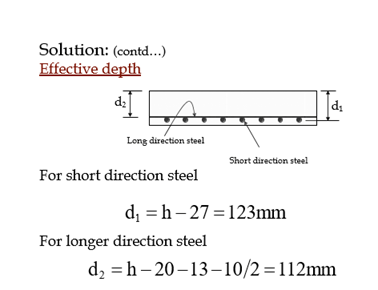
Solution: (contd…)
Slab Thickness
Generally same depth is preferred for one monolith slab. Calculate hmin for all the
panels and select the largest value.


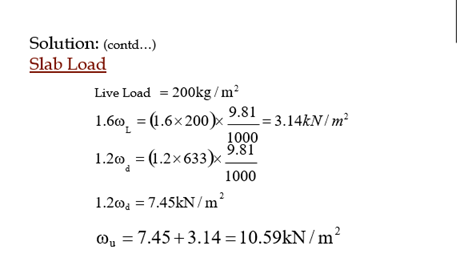
Solution: (contd…)
Minimum Steel
As min= 0.002bh
As min= 0.002 ´1000 ´150
As min= 300mm2For a unit strip
Concluded