Description
-
 MS Office Home & Business 2024 – Lifetime License Key – Mac/PC$150.00 – $160.00
MS Office Home & Business 2024 – Lifetime License Key – Mac/PC$150.00 – $160.00 -
![Guide for Design of Slab-Column Connections in Monolithic Concrete Structures 4 [Retail] Office 2021/2019/2016 Pro Plus Activates 5 PCs Online](https://civilmdc.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/05/Microsoft-Office-professional-plus-all-in-one-free-download-e1717158603220-300x300.jpg) [Retail] Office 2021/2019/2016 Pro Plus Activates 5 PCs Online$50.00 – $120.00
[Retail] Office 2021/2019/2016 Pro Plus Activates 5 PCs Online$50.00 – $120.00 -
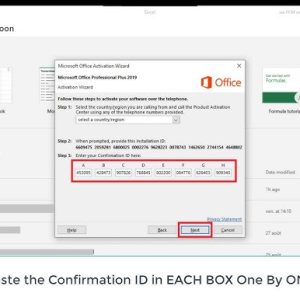 Microsoft office /Windows Activation Service for Phone Activation Method (Get Confirmaiton ID)$3.00
Microsoft office /Windows Activation Service for Phone Activation Method (Get Confirmaiton ID)$3.00 -
 MS SQL Server 2022 Standard | 1 Key for 1 PC$80.00
MS SQL Server 2022 Standard | 1 Key for 1 PC$80.00 -
 Youtube Premium | 4 months Premium Membership$10.00
Youtube Premium | 4 months Premium Membership$10.00 -
Product on sale
 Adobe Stock 40 creditsOriginal price was: $99.00.$20.00Current price is: $20.00.
Adobe Stock 40 creditsOriginal price was: $99.00.$20.00Current price is: $20.00. -
Product on sale
 MS Office 2021 Home & Business 1 MAC Bind for iOSOriginal price was: $429.00.$85.00Current price is: $85.00.
MS Office 2021 Home & Business 1 MAC Bind for iOSOriginal price was: $429.00.$85.00Current price is: $85.00. -
 MS Office 365 Personal | Family Plan on Your Email Id – 1 Year subscription$30.00 – $66.00
MS Office 365 Personal | Family Plan on Your Email Id – 1 Year subscription$30.00 – $66.00 -
 MS Project Professional 2024 | 2021 | 2019 | 2016 1 PC Online key Activation$20.00 – $55.00
MS Project Professional 2024 | 2021 | 2019 | 2016 1 PC Online key Activation$20.00 – $55.00 -
Product on sale
 Adobe Creative Cloud (All apps) – PersonalOriginal price was: $560.00.$200.00Current price is: $200.00.
Adobe Creative Cloud (All apps) – PersonalOriginal price was: $560.00.$200.00Current price is: $200.00. -
 Windows Server 2019 Online Key$22.00
Windows Server 2019 Online Key$22.00 -
 MS Office Visio Professional 2024 | 2021 | 2019 | 2016 PC Online Key Activation$20.00 – $45.00
MS Office Visio Professional 2024 | 2021 | 2019 | 2016 PC Online Key Activation$20.00 – $45.00 -
Product on sale
 MS 2019 Project Professional Windows 1 PC Online keyOriginal price was: $429.00.$22.00Current price is: $22.00.
MS 2019 Project Professional Windows 1 PC Online keyOriginal price was: $429.00.$22.00Current price is: $22.00. -
 McAfee LiveSafe Internet Security Antivirus 1 PC – 10 YEARS – Key$29.00
McAfee LiveSafe Internet Security Antivirus 1 PC – 10 YEARS – Key$29.00 -
 Office Professional 2016 /2013/2010 – Lifetime License Key – 1PC$14.00 – $16.00
Office Professional 2016 /2013/2010 – Lifetime License Key – 1PC$14.00 – $16.00
The recommendations in this guide are for determining connection proportions and details to provide adequate performance of cast-in-place reinforced concrete (RC) and post-tensioned concrete (PT) slab-column connections. The recommendations are written to satisfy serviceability, strength, and ductility requirements related to the intended functions of the connection.
Design of the connection between a slab and its supporting member requires consideration of both the joint and the portion of the slab, or slab and beams, immediately adjacent to the joint. Several connection failures associated with inadequate performance of the slab adjacent to the joint have been reported (Engineering News-Record (ENR) 1956,1971, 1973; Joint ACI-ASCE Committee 426 1974; Leyen-decker and Fattal 1977; Lew et al. 1982a,b; Rosenblueth and Meli 1986; Freyermuth 1989; Moehle 1996; Hueste and Wight 1997).
However, no reported cases of connection failure due to distress within the joint have been identified. Some connection failures have occurred during construction when young concrete slabs received loads from more than one floor as a consequence of shoring and reshoring (Agarwal and Gardner 1974; Lew et al. 1982a,b; Sbarounis 1984; ACI 347-05). The disastrous consequences of some failures, including total collapse of the structure, empha-size the importance of the design of the connection. These recommendations are intended to alert the designer to those aspects of behavior that should be considered in design of the connection and to suggest design procedures that will lead to adequate connection performance
-
 Bitdefender Total Security Antivirus | Genuine Activation Code$30.00
Bitdefender Total Security Antivirus | Genuine Activation Code$30.00 -
 IDEA StatiCa Education$30.00
IDEA StatiCa Education$30.00 -
 Stealth Writer AI | Bypass AI Detection | Get 100% Human Score$10.00
Stealth Writer AI | Bypass AI Detection | Get 100% Human Score$10.00 -
 Adobe Acrobat XI Professional with License Key Activation$29.00
Adobe Acrobat XI Professional with License Key Activation$29.00 -
 Autocad 2007 – OFFLINE INSTALLER + Video Tutorial Install and activation – LIFETIME$7.00
Autocad 2007 – OFFLINE INSTALLER + Video Tutorial Install and activation – LIFETIME$7.00 -
 ChatGPT PLUS Subscription$7.00
ChatGPT PLUS Subscription$7.00 -
 ESET Internet Security Antivirus | 1 Year License$20.00
ESET Internet Security Antivirus | 1 Year License$20.00 -
 Course Hero Account 📗1 month$10.00
Course Hero Account 📗1 month$10.00 -
 General Software Collection | Request books, Codes, Research Articles | Request Software on Demand$3.00 – $35.00
General Software Collection | Request books, Codes, Research Articles | Request Software on Demand$3.00 – $35.00 -
 Vmware Workstation 16 Pro Lifetime License$150.00 – $199.00
Vmware Workstation 16 Pro Lifetime License$150.00 – $199.00 -
 NORD VPN/IP Vanish Account Subscription 6 Month | 1 Year | 2 Years$20.00 – $60.00
NORD VPN/IP Vanish Account Subscription 6 Month | 1 Year | 2 Years$20.00 – $60.00 -
 Internet Download Manager IDM Version 6.41 fully lifetime activation with installation video | 5 times faster download (Pre-Activated)$6.00
Internet Download Manager IDM Version 6.41 fully lifetime activation with installation video | 5 times faster download (Pre-Activated)$6.00 -
 Adobe Acrobat Pro DC 2024 | 2023 | 2022 | 2021 | 2020 | Latest Full Version | Lifetime$10.00 – $20.00
Adobe Acrobat Pro DC 2024 | 2023 | 2022 | 2021 | 2020 | Latest Full Version | Lifetime$10.00 – $20.00 -
![Guide for Design of Slab-Column Connections in Monolithic Concrete Structures 31 Sketch Up Pro 2025 | 2024 | 2023 | 2022 | 2021 Full Package Bundle + Vray 7 + Enscape 4.4 + Thea Render 3.5 [Lifetime & Full]](https://civilmdc.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/03/SketchUp-2025-300x300.jpg) Sketch Up Pro 2025 | 2024 | 2023 | 2022 | 2021 Full Package Bundle + Vray 7 + Enscape 4.4 + Thea Render 3.5 [Lifetime & Full]$10.00 – $45.00
Sketch Up Pro 2025 | 2024 | 2023 | 2022 | 2021 Full Package Bundle + Vray 7 + Enscape 4.4 + Thea Render 3.5 [Lifetime & Full]$10.00 – $45.00 -
 Adobe 2024 | 2023 | 2022 Full Collection$25.00 – $35.00
Adobe 2024 | 2023 | 2022 Full Collection$25.00 – $35.00


