Macro 32: Creating and Selecting Named Ranges
One of the more useful features in Excel is the ability to name your range (that is, to give your range a
user-friendly name, so that you can more easily identify and refer to it via VBA).
Here are the steps you would perform to create a named range manually.
1. Select the range you wish to name.
2. Go to the Formulas tab in the Ribbon and choose the Define Name command (see
Figure 4-1).
3. Give the chosen range a user-friendly name in the New Name dialog box, as shown in Figure
4-2.
When you click OK, your range is named. To confirm this, you can go to the Formula tab and select the
Name Manager command. This activates the Name Manager dialog box (see Figure 4-3), where you can
see all the applied named ranges.
Figure 4-1: Click the Define Name command to name a chosen range.
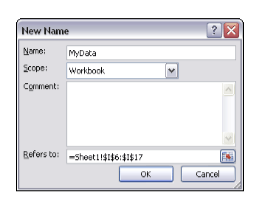
Figure 4-2: Give your range a name.
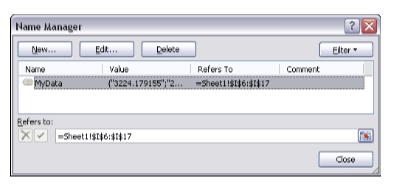
Figure 4-3: The Name Manager dialog box lists all the applied named ranges.
Creating a named range via VBA is much less involved. You can directly define the Name property of
the Range object:
Sub Macro32a()
Range(“D6:D17”).Name = “MyData”
End Sub
Admittedly, you’d be hard pressed to find a situation where you would need to automate the creation
of named ranges. The real efficiency comes in manipulating them via VBA.
How it works
You simply pass the name of the range through the Range object. This allows you to select the range:
Sub Macro32b()
Range(“MyData”).Select
End Sub
As with normal ranges, you can refer to the range using the With…End With statement. This state-
ment tells Excel that any action you perform applies to the object to which you’ve pointed. This not
only prevents you from having to repeat syntax, but it also allows for the easy addition of actions by
simply adding them between the With and End With statements.
Sub Macro32a()
With Range(“MyData”)
.NumberFormat = “#,##0”
.Font.Bold = True
.Interior.ColorIndex = 36
End With
End Sub
How to use it
To implement this kind of a macro, you can copy and paste it into a standard module:
1. Activate the Visual Basic Editor by pressing ALT+F11.
2. Right-click the project/workbook name in the Project window.
3. Choose Insert➜Module.
4. Type or paste the code.

